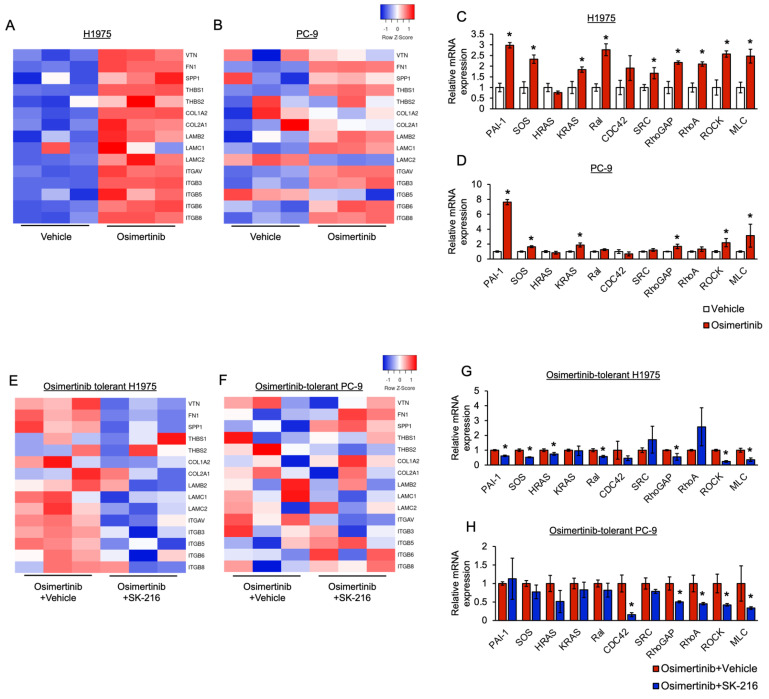
Figure 4.
Involvement of PAI-1 in tolerance to EGFR-TKI via its association with integrin-initiated EMT. (A,B) From the microarray results, the mRNA expression levels of integrins αVβ3, αVβ6, and αVβ8 and extracellular matrix components were extracted and are shown in a heat map. In each of (A) H1975 and (B) PC-9, untreated controls were compared to osimertinib-tolerant cells. Blue represents downregulated genes; red represents upregulated genes. (C,D) qRT-PCR analysis of the mRNA expression of PAI-1 and integrin-initiated EMT-related genes in osimertinib-tolerant and untreated control (C) H1975 and (D) PC-9 cells. The relative expression level of each gene is shown with standard error bars (n = 4), compared with untreated control cells; * p < 0.05 (Student’s t-test). (E,F) From the microarray results, the mRNA expression levels of integrins and extracellular matrix components were extracted and are shown in a heat map. For (E) osimertinib-tolerant H1975 and (F) osimertinib-tolerant PC-9, untreated controls were compared to SK-216-treated cells. Blue represents downregulated genes; red represents upregulated genes. (G,H) qRT-PCR analysis of the expression of PAI-1 and integrin-initiated EMT-related genes in osimertinib-tolerant (G) H1975 and (H) PC-9 cells. Osimertinib-tolerant cells were treated with SK-216 combined with osimertinib, and mRNA expression was evaluated 48 h after SK-216 administration. The relative expression level of each gene is shown with standard error bars (n = 4); * p < 0.05 compared with cells exposed to vehicle controls (Student’s t-test).