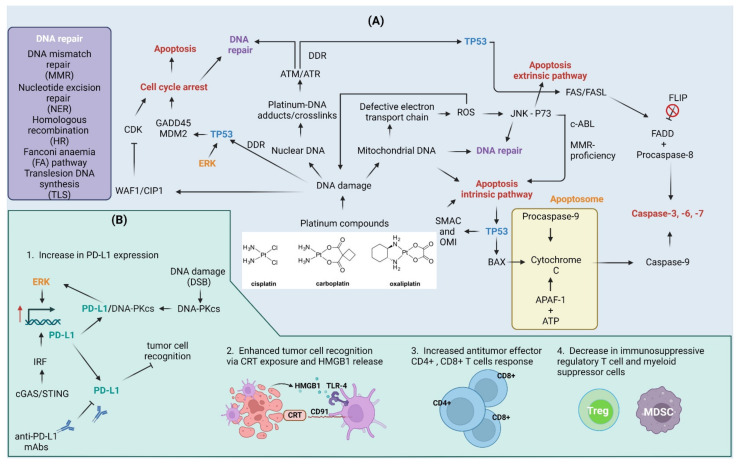
Figure 3.
Cellular and immune response to platinum compounds. (A) Cellular response to platinum compounds: Platinum compounds induce DNA damage to both nuclear and mitochondrial DNA. Mitochondrial DNA damage can lead to defects in the electron transport chain that contribute to electron leakage and the formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). ROS contribute to DNA damage in both nuclear and mitochondrial DNA in a feedback mechanism. ROS also act as molecular messengers and contribute to the activation of the Jun amino-terminal kinase (JNK) pathway that together with the P73 protein trigger apoptotic cell death. C-ABL kinase activity and mismatch repair (MMR)-proficiency are required for cell death to occur. DNA damage activates DNA damage response (DDR), as indicated by the activation of serine/threonine kinases ATM and ATR. The outcome of DDR relies heavily on cellular tumor antigen p53 (TP53) protein: (a) activation of TP53 in response to DNA damage triggers cell cycle arrest through up-regulation of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1 (WAF1/CIP1), 45kd-growth arrest, and DNA damage (GADD45) and mouse double minute 2 homolog (MDM2) or via WAF1/CIP1-mediated inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs); (b) subsequent DNA repair via co-operation of nucleotide excision repair (NER), MMR, homologous recombination (HR), Fanconi anemia (FA) pathway, or translesion synthesis (TLS); or (c) apoptosis induction through intrinsic apoptosis pathway followed by ROS-damage accumulation, TP53-dependent up-regulation of Bcl2-associated agonist of cell death (BAD), Diablo IAP-binding mitochondrial protein (SMAC) and serine protease HTRA2 (OMI), or through activation of FASL/FAS extrinsic apoptosis pathway. Cisplatin induces flice-like inhibitory protein (FLIP) ubiquitination and degradation, which further activate the extrinsic pathway. (B) Effect of platinum compounds on the antitumor immune response: Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS)/stimulator of interferon genes protein (STING) pathway and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) signaling up-regulate programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1) expression. The DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit (DNA-PKcs) up-regulated in response to double-strand breaks (DSBs) associates with PD-L1 conferring to the activation of the ERK pathway and further up-regulation of PD-L1. This, on the one hand, contributes to immune evasion, but also increase the therapeutic efficiency of anti-PD-L1 monoclonal antibodies (mAbs). Platinum compounds also enhance tumor recognition through calreticulin (CRT) exposure on cell surface and high mobility group protein 1 (HMGB1) release, induce CD4+/CD8+ T cell response, and suppress regulatory T cells (Treg) and myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSC). APAF-1—apoptotic protease-activating factor 1; FADD—FAS-associated death domain protein. Created with BioRender.com accessed on 1 February 2023.