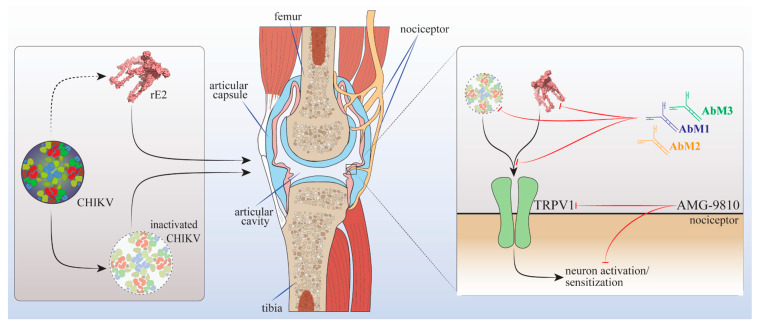
Figure 8.
Schematic summary proposal of Chikungunya virus-induced pain. Intra-articular administration of inactivated Chikungunya virus (iCHIKV) and recombinant E2 (rE2) protein induce mechanical and thermal hyperalgesia in Swiss mice and C57BL/6 mice. Treatment with the three anti-E2 antibodies (mAb1, mAb2, and mAb3) reduced iCHIKV- and rE2-induced hyperalgesia demonstrating the contribution of E2 to the pain caused by the Chikungunya virus. iCHIKV and rE2 pain depend on direct activation of TRPV1+ DRG neurons as observed by genetic ablation (TRPV1 deficiency), pharmacological treatment (AMG-9810), behavioral analysis, and neuronal activity.