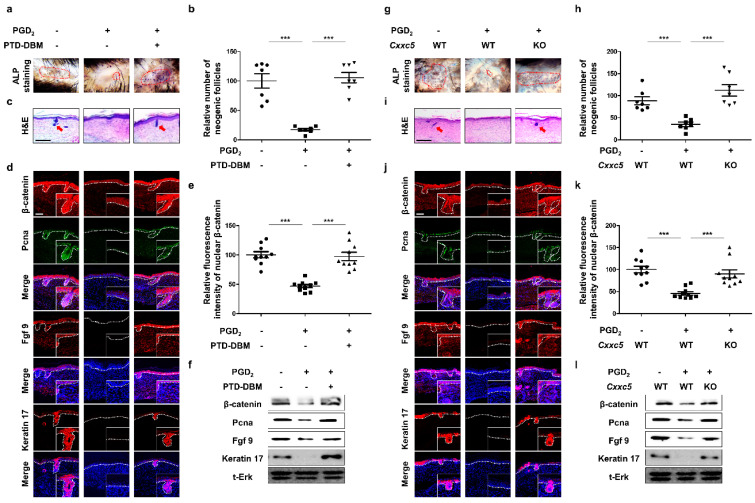
Figure 4.
Effects of inhibition of Cxxc5 function on wound-induced hair neogenesis. (a–f) The dorsal skins of 3-week-old C57BL/6N wild-type mice were wounded and harvested at 21 or 25 days. Topical treatment of 10 μg PGD2 or 10 mM PTD-DBM was conducted from 7 days to 21 or 25 days daily after wounding. (a,b) ALP staining of neogenic follicles 25 days after wounding (n = 7). (c) H&E staining of wounded skin 21 days after wounding. (d) IHC staining for Pcna, β-catenin, keratin 17, and Fgf9 at 21 days. (e) Quantitative calculations for nuclear β-catenin (n = 10). (f) Immunoblotting analyses for β-catenin, Pcna, Fgf9, keratin 17, and total Erk at 21 days. (g–l) The back skins of Cxxc5 wild-type or knock-out mice were cut and harvested at 21 or 25 days after wounding. Treatment with 10 μg PGD2 was performed from 7 days to 21 or 25 days. (g,h) ALP staining for neogenic follicles at 25 days (n = 7). (i) H&E staining of dorsal skins at 21 days. (j) IHC analyses for keratin 17, Fgf9, β-catenin, and Pcna at 21 days. (k) Quantitative values for nuclear β-catenin (n = 10). (l) Immunoblotting assay for Fgf9, keratin 17, Pcna, β-catenin, and total Erk at 21 days. Scale bars = 100 µm. Dotted lines represent ALP-positive newly formed hair (a,g) or the boundary between the dermis and epidermis (d,j). Arrows indicate neogenic hair. Values are expressed as means ± SEM. Student’s t-tests: *** p < 0.0005.