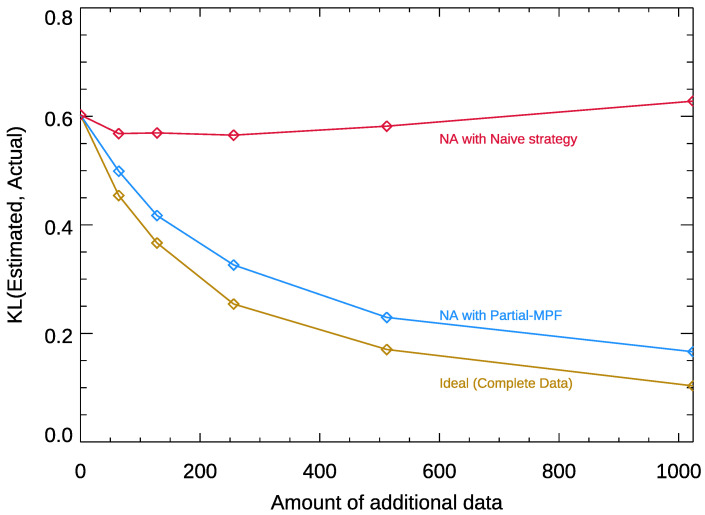
Figure 2.
An example of how Partial-MPF adapts the baseline MPF algorithm to make use of partial data. We begin with 128 complete samples of a particular 20-question landscape (drawn from a distribution with equal to 0.2), and then add additional, incomplete samples where five of the 20 questions are marked unknown. As more, but incomplete, data is added, the Partial-MPF fit (blue line) continues to improve, though not as fast as when the additional data is complete (yellow line). By contrast, the naive strategy (red line) often makes the fit worse, because imputation destroys implicit correlations.