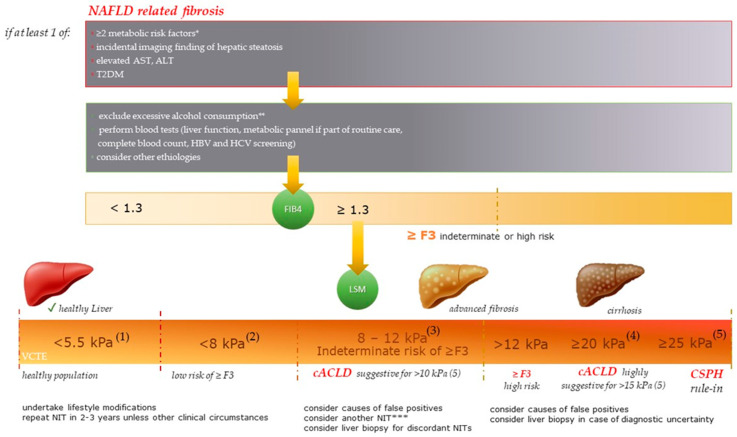
Figure 4.
Screening algorithm for NAFLD-related Fibrosis. * the metabolic conditions include central obesity—waist circumference with ethnicity-specific cut-offs, serum triglycerides ≥150 mg/dL or specific treatment for hypertriglyceridemia, reduced serum high-density lipoprotein cholesterol <40 mg/dL in males (<50 mg/dL in females) or those undergoing a specific treatment, systolic blood pressure ≥130 mmHg, or diastolic blood pressure ≥85 mmHg or specific treatment, raised fasting plasma glucose between 100 mg/dL and 125 mg/dL (prediabetes) [128,129]; T2DM—type two diabetes mellitus; AST—aspartate aminotransferase; ALT—alanine aminotransferase; ** ≥30 g/day for men and ≥20 g/day for women; HBV—hepatitis B virus; HCV—hepatitis C virus; FIB4—Fibrosis-4 Index; LSM—liver stiffness measurement; T2DM—type two diabetes mellitus; VCTE—vibration-controlled transient elastography, whereby the values obtained with the XL probe are usually lower than those with the M probe [26]. (1) shear wave elastography (SWE) within the normal range can rule out significant liver fibrosis when in it is in agreement with the clinical and laboratory background [26], an LS ≤ 5 kPa presents high probability of being normal as recommended in the “rule of four” for acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) techniques [28], (2) VCTE < 8 kPa rules out advanced fibrosis in NAFLD [123], (3) the 8 kPa and 12 kPa dual cut-offs have a better diagnostic accuracy of NAFLD-related cACLD than the previously established cut-offs do [115] (cACLD is a term introduced in 2015 to describe the spectrum of advanced fibrosis (≥F3) and cirrhosis (F4) in compensated patients) (4) cut-off result from a recently published meta-analysis [130], and (5) according to the Baveno VII criteria [51], *** ELFTM < 9.8 or FibroMeterTM < 0.45 or FibroTest® < 0.48 to rule-out ≥F3 in NAFLD [123]. CSPH—clinical significant portal hypertension.