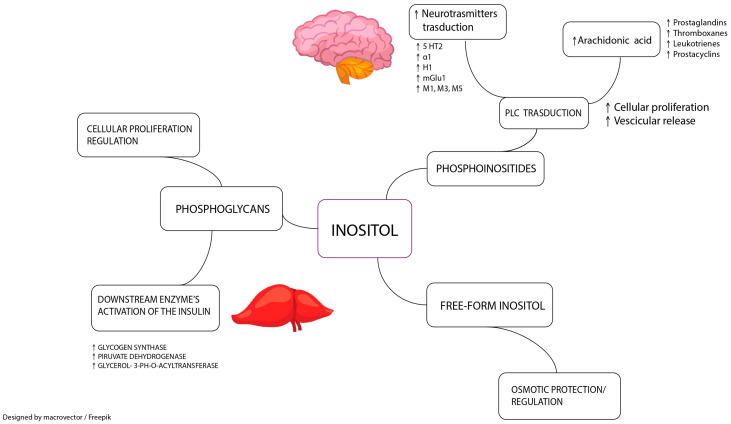
Figure 1.
Different roles of inositol and inositol-containing molecules in human physiology. Free-form inositols, such as Myo-inositol and D-chiro-inositol, act as osmolytes to ensure adequate cellular defense against external and/or metabolic stressors. Phosphoglycans are involved in glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol/inositol phosphoglycans pathway as second messengers, regulating different cellular pathways, including insulin sensitization and cellular proliferation regulation. As phosphoinositide, inositol plays a role in phospholipase transduction, which is the signal transduction pathway of many neurotransmitter receptors. The cleavage of phosphoinositide by phospholipase activation can also release arachidonic acid, which can be subsequently converted into many inflammation mediators. M1, M3, M5: acetylcholine ionotropic receptors; H1: histamine ionotropic receptor; α1: norepinephrine ionotropic receptor; 5HT2: serotonin ionotropic receptor; mGlu1: glutamate metabotropic receptor; ↑: increase.