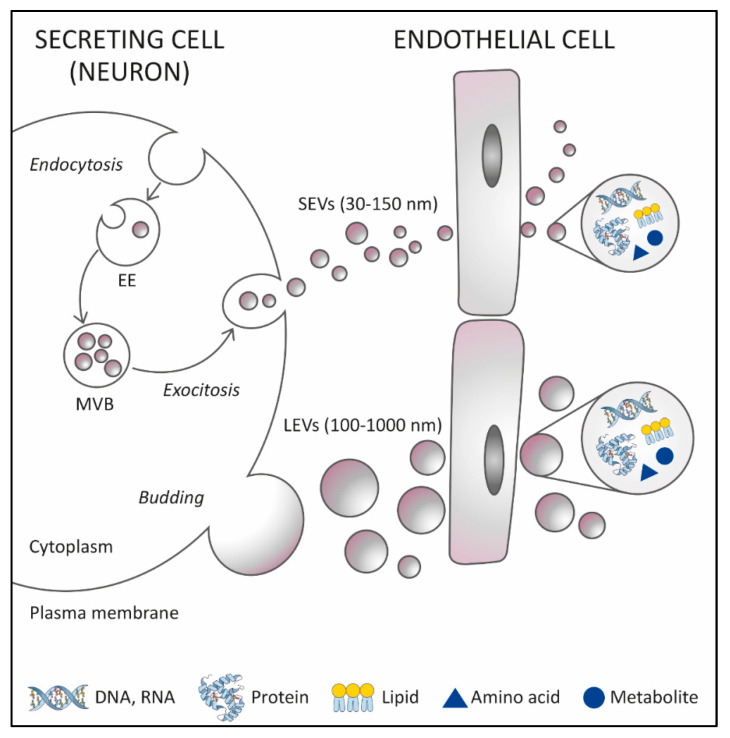
Figure 1.
Formation of extracellular vesicles (EVs) and transport across the blood–brain barrier (BBB). Large EVs (LEVs) and small EVs (SEVs) are two subtypes of EVs, that can be distinguished by their size and biogenesis. LEVs are shed by budding of the plasma membrane, whereas SEVs are formed intracellularly and released by exocytosis of multivesicular bodies (MVBs). EVs can cross the BBB and thus enable various components, specific to secreting cells, including nucleic acids, proteins, amino acids, lipids, and metabolites in the EVs to be transported from the central nervous system (CNS) to peripheral biofluids. EE, early endosome.