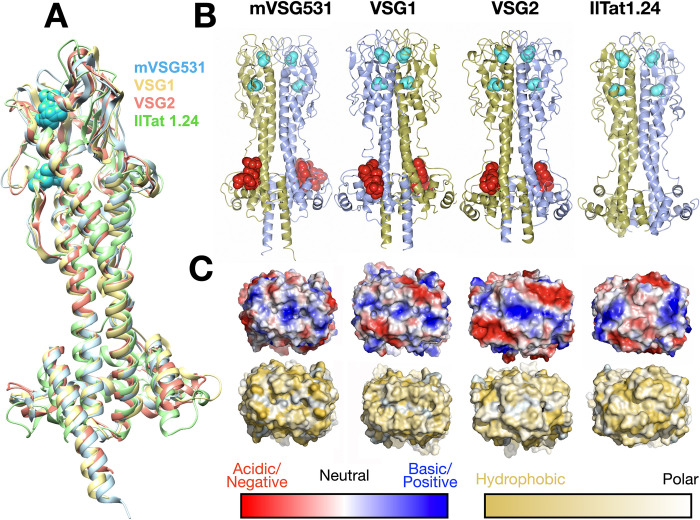
Fig 3. Crystal structure of mVSG531.
(A) Superposition of class A2/N2 monomers of mVSG531, VSG1, VSG2, and IlTat1.24 produced using DeepAlign in the RaptorX structure alignment server [48,49]. Images of protein structures were generated and edited using CHIMERA [61]. (B) Side-by-side comparison of different class A VSG dimer highlighting common fold, disulfide placement (cyan spheres), and N-linked glycan (red spheres). Structures drawn with CCP4mg [57]. (C) 90-degree rotation of the structures in (B) to view the “top” surface of the VSG, rendered as a molecular surface. Top row shows the surface colored by contact potential (red indicating acidic/negatively charged, blue indicating basic/positively charged, and white neutral, all surfaces scaled identically). The bottom row is colored by the Eisenberg hydrophobicity scale [59], where yellow indicates hydrophobic and white polar. Molecular surfaces are illustrated with PyMOL [60].