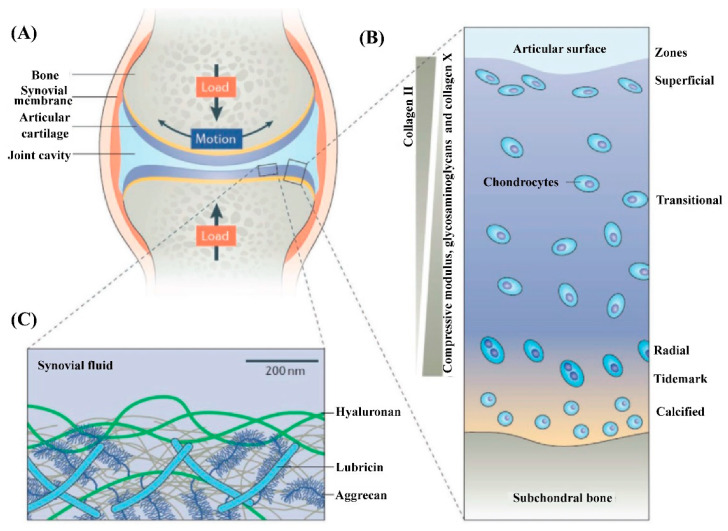
Figure 1.
Illustration of the components and structure of AC. (A) The knee synovial joint is mainly composed of the synovial membrane, AC, and the synovial fluid within the synovial cavity. (B) AC is characterized by its layered structure. Chondrocytes make up less than 5% (volume fraction) of AC. The main composition of ECM, type II collagen, glycosaminoglycans, collagen X, and the depth-dependent modulus, are indicated. (C) Illustration of the outer surface of AC that determines the lubrication performance of AC. Glycosaminoglycans, including hyaluronic acid (HA) and aggrecan, as well as lubricin and phospholipids (are not shown here) synergically assemble to form a lubrication layer outer of the AC surface to determine its remarkable lubrication at high pressure. Reprinted with permission from Ref [4]. Copyright 2021, Wiley-VCH.