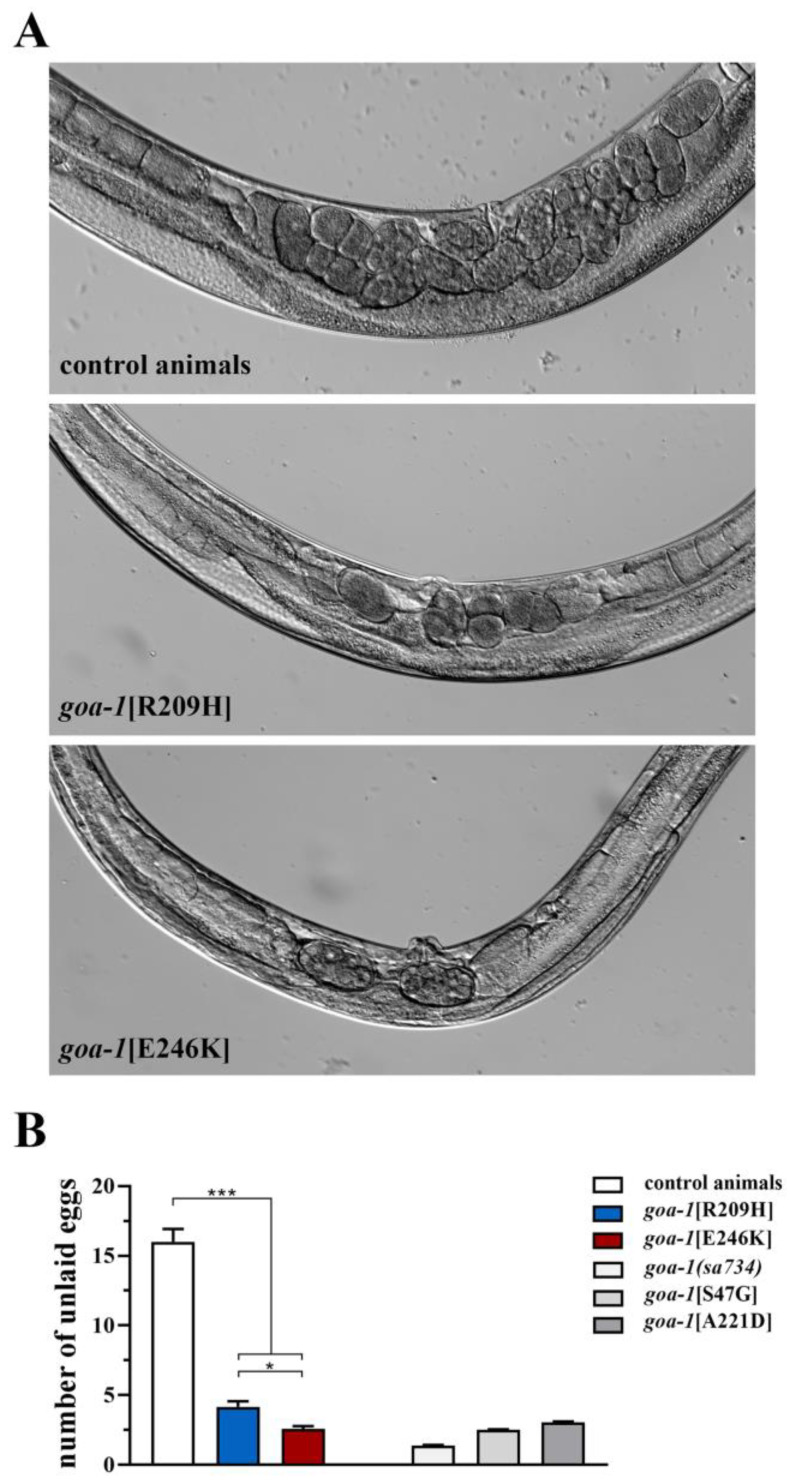
Figure 1.
goa-1[R209H] and goa-1[E246K] animals show increased egg laying activity. (A) Representative images of mid-body regions of control animals (upper panel) and goa-1 mutants (lower panels). Retained eggs are visible as oval objects inside the body of adult hermaphrodites. Wild-type worms displayed 15 unlaid eggs on average, while Gαo mutants retained only a few eggs in their uterus. Magnification is constant in all images. (B) The egg laying activity is quantified as the number of eggs present in the uterus (* p < 0.05 and *** p < 0.0001; one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni correction). Twenty animals for each genotype were tested. Data represent means ± SEM of multiple observations. Data collected in our previous study [18] are included in panel B for comparison (gray bars). sa734 is a null allele of goa-1 [30,32].