Figure 3.
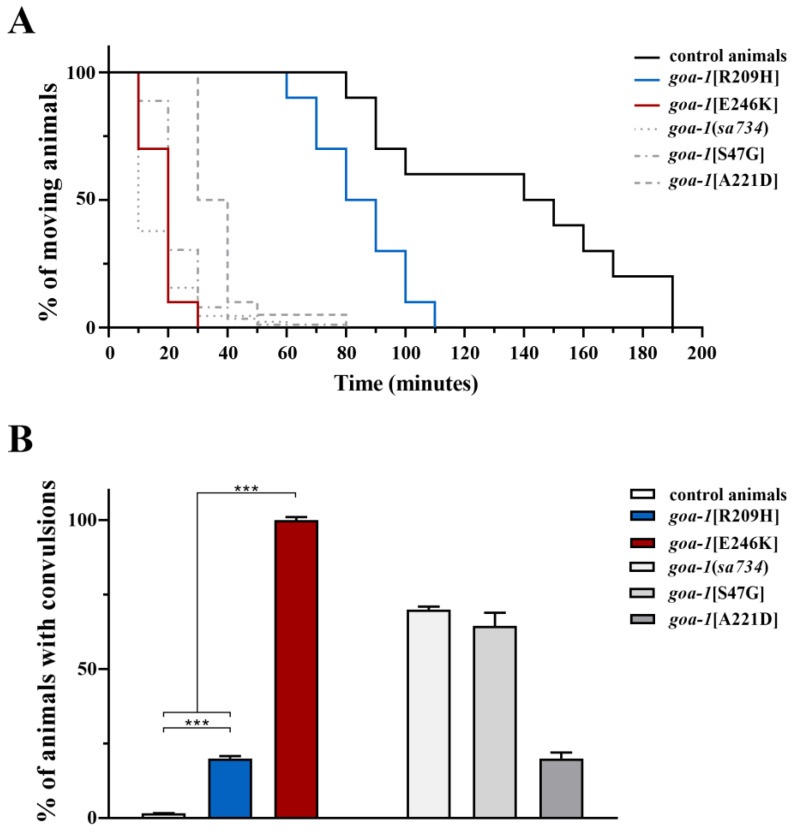
goa-1[R209H] and goa-1[E246K] animals display increased ACh release at the NMJ. (A) Gαo mutants showed hypersensitivity to aldicarb (1 mM) compared with control animals (p < 0.005 for goa-1[R209H] and p < 0.0001 for goa-1[E246K]; log-rank test), suggesting increased ACh release at the C. elegans NMJ. Twenty animals for each genotype were tested. (B) Gαo mutants showed hypersensitivity to PTZ (5 mg/mL on agar plates; 15 min of exposition), likely indicating an excess of stimulatory signal over inhibitory signal at the NMJ (*** p < 0.0001; Fisher’s exact test with Bonferroni correction). In both assays, goa-1[E246K] animals displayed a much more severe phenotype than goa-1[R209H] worms (p < 0.0001). Twenty animals for each genotype were tested. Data represent means ± SEM of three independent experiments. Data collected in our previous study [18] are included for comparison (gray bars). Sa734 is a null allele of goa-1 [30,32].