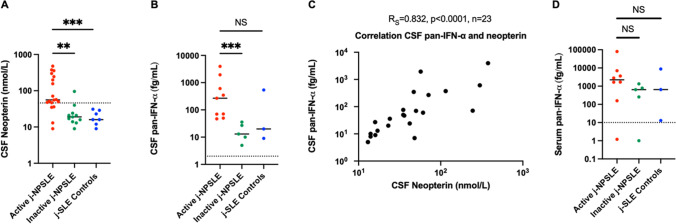
Fig. 1.
Comparison of CSF neopterin and IFN-α concentrations in non-NPSLE (j-SLE controls), active and inactive j-NPSLE patients. A Comparison of CSF neopterin concentration assessed by liquid chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry during active j-NPSLE in red (n = 18), inactive j-NPSLE in green (n = 11) and in non-NPSLE patients in blue (j-SLE controls, n = 7). B CSF pan-IFN-α concentration during active j-NPSLE in red (n = 9), inactive j-NPSLE in green (n = 5) and in non-NPSLE patients in blue (j-SLE controls, n = 3). C Correlation of pan-IFN-α measurement with neopterin assessment in the CSF in patients with j-NPSLE (n = 21) and j-SLE without NPSLE (n = 2). Spearman’s correlation was calculated Rs = 0.832, p < 0.0001, n = 23. D Serum pan-IFN-α concentration during active j-NPSLE in red (n = 8), inactive j-NPSLE in green (n = 5) and in non-NPSLE patients in blue (j-SLE controls, n = 3). Median levels are indicated by horizontal black bars, normal levels are indicated by horizontal dotted line. For A, B, D, tests were performed two by two with a Mann–Whitney’s test: the first compared active j-NPSLE and inactive j-NPSLE, the second test compared active j-NPSLE and j-SLE controls. *p < 0.05, ** < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, NS non-significant. CSF cerebrospinal fluid; IFN interferon; j-NPSLE juvenile neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus; j-SLE juvenile systemic lupus erythematosus; Simoa single-molecule array