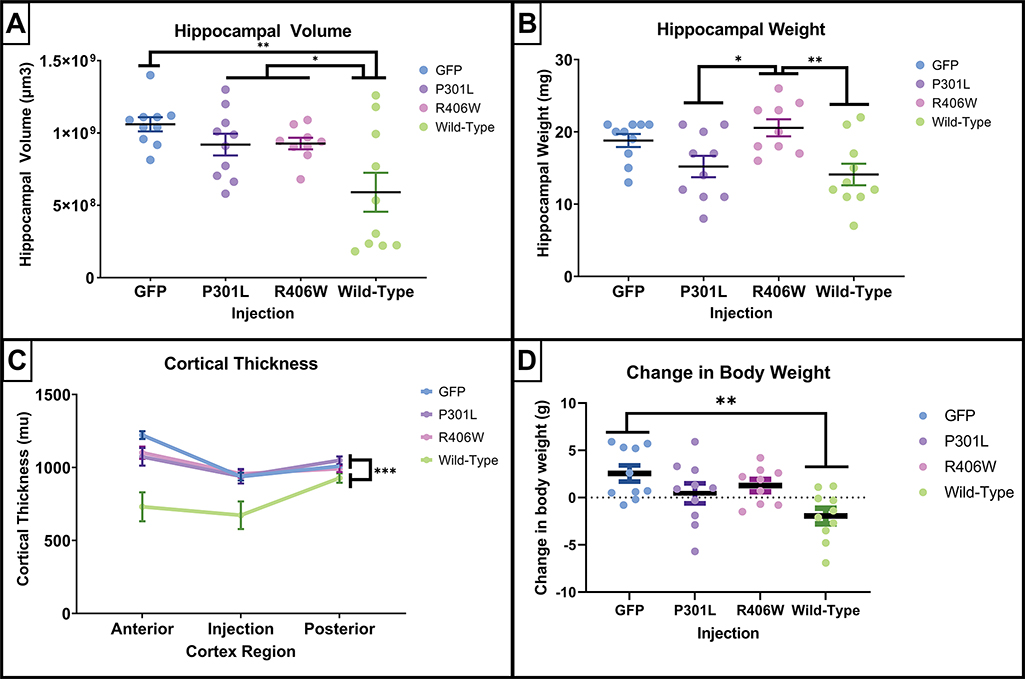
Figure 3.
Quantification of indicators of atrophy following intracranial AAV-tau injections. The tauwild-type intracranial injection exhibited the greatest amount of atrophy. (A, B, and D) scatterplots of individual animal’s expression values are plotted by injection groups for panels. Each dot represents one mouse. Data are presented as mean ±SEM (error bars). (A) Quantification of hippocampal volume estimated using 8 sections spanning the entire hippocampus by the method of Cavalieri indicated that the tau wild-type mice had a significant reduction of hippocampal volume compared to the other injections. (B) The hippocampal weights measured in milligrams demonstrated that tauP301L and tauwild-type mice had the lowest hippocampal weights. (C) The cortical thickness measured in micrometers anterior to the cortical injection site, the injection site, and posterior to the injection site confirmed the loss of cortical volume in the tauwild-type mice. (D) The change in body weight in grams prior to receiving intracranial injection compared to the weight at the time of tissue collection. Results from one-way ANOVA (A, B, and D) and one-way repeated mixed measures ANOVA (C). Results. * p<.05 * p<0.05, **p<0.01, *** p≤0.001 Tukey’s post-hoc analyses.