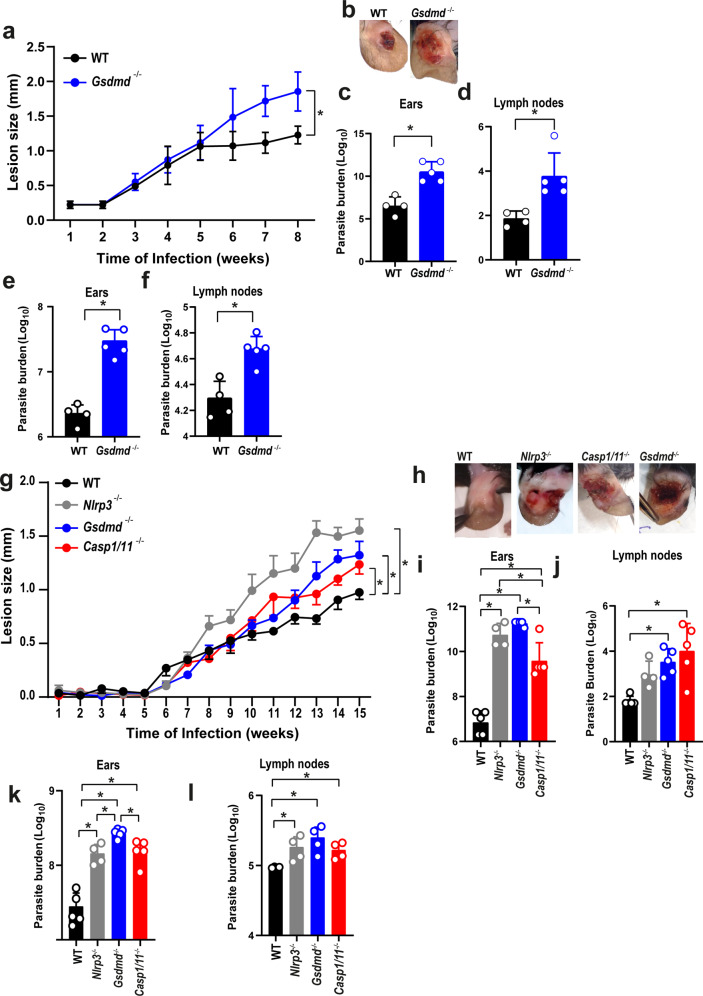
Fig. 6. GSDMD is important for the restriction of L. amazonensis infection in vivo.
a–f C57BL/6 (WT) and Gsdmd–/– mice were infected with 106 stationary-phase L. amazonensis promastigotes in the ear, and the ear thicknesses were followed for 8 weeks. a Lesion development; b images of infected ears; c, d limiting dilution analysis of parasite burden in the infected ears (c), and draining lymph nodes (d); e, f parasite quantification by real-time PCR in the infected ears (e), and draining lymph nodes (f) at 8 weeks of infection. Each dot in the bar graphics represents the value obtained from an individual mouse. Data are presented as mean values ± SD. #P < 0.05 compared with WT mice; *P < 0.05 comparing the indicated groups, as determined by the Student T test two-sided. g, l C57BL/6 (WT), Nlrp3–/–, Casp1/11–/–, and Gsdmd–/– mice were infected with 103 metacyclic L. amazonensis promastigotes in the ear, and the ear thicknesses were followed for 15 weeks. g Lesion development; (h) images of infected ears; i, j limiting dilution analysis of parasite burden in the infected ear (i) and draining lymph nodes (j); k, l parasite quantification by real-time PCR in the infected ears (k), and draining lymph nodes (l) at 15 weeks of infection. Each dot in the bar graphics represents the value obtained from an individual mouse. Data are presented as mean values ± SD. *P < 0.05 comparing the indicated groups, as determined by two-way ANOVA. Shown is one representative experiment of five independent experiments performed. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.