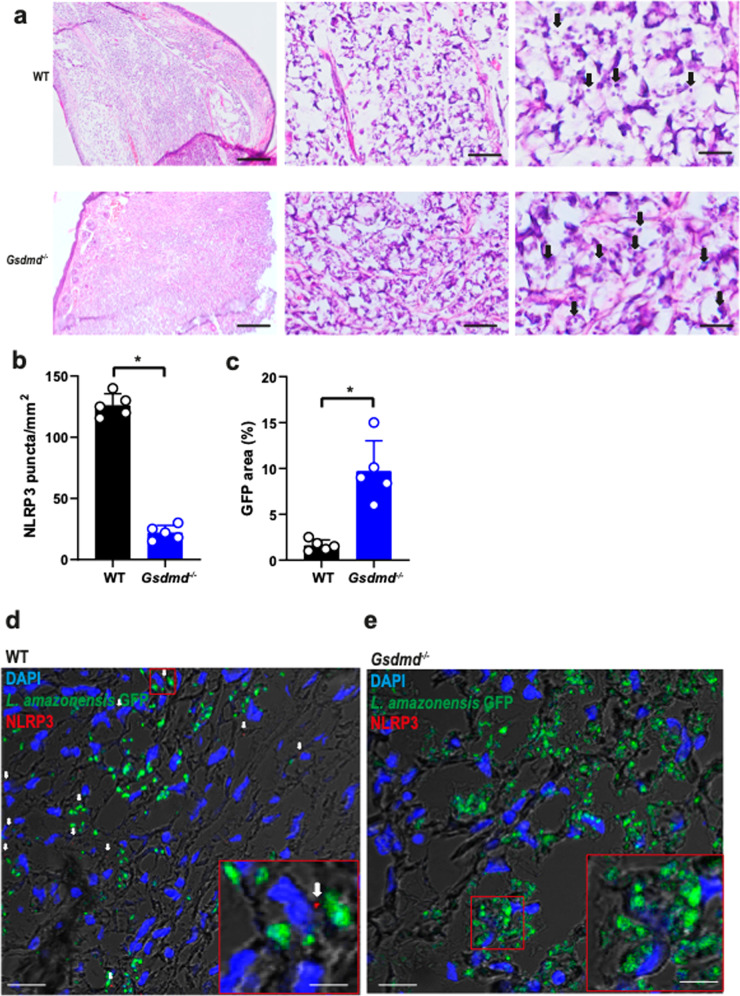
Fig. 7. GSDMD is important for the restriction of L. amazonensis infection and NLRP3 inflammasome activation in vivo.
C57BL/6 (WT) and Gsdmd–/– mice (n = 5 mice per group) were infected with 106 stationary-phase promastigotes of L. amazonensis-expressing GFP. (a) Hematoxylin and Eosin staining of the infected ear indicates the amastigotes (arrows). Scale bars, 500, 50, and 20 µm (from left to right). b–e Multiphoton microscopy of infected ears stained with anti-NLRP3 for quantification of NLRP3 puncta formation (b) and percentage of GFP area (c). Representative images of WT (d) and Gsdmd–/– mice (e) showing NLRP3 puncta (in red, indicated by a white arrow). GFP-expressing Leishmania is shown in green, and DAPI stains cell nuclei (blue). Scale bar 40 µm. Insets indicate a higher magnification of a region indicated (red rectangle, scale bar 20 µm). Each dot in the figure represents the value obtained from an individual mouse. Data are presented as mean values ± SD. *P < 0.05 comparing the indicated groups, as determined by the Student T test two-sided. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.