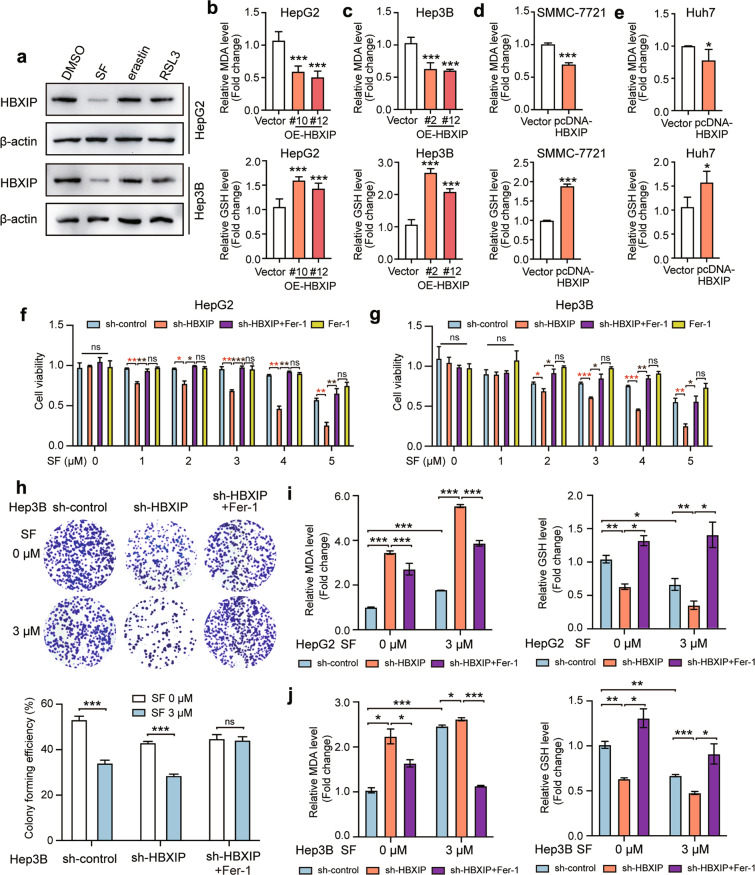
Fig. 2. HBXIP is involved in ferroptosis suppression in sorafenib-treated HCC cells.
a WB analysis was applied to analyze the expression of HBXIP in HepG2 and Hep3B cells with DMSO, SF, erastin or RSL3 (the activators of ferroptosis) for 48 h. b, c MDA and GSH were detected in HepG2, Hep3B cells and two stable HBXIP overexpression clones. d, e MDA and GSH were detected in SMMC-7721 and Huh7 cells transfected with pcDNA-Vector or pcDNA-HBXIP for 48 h. f, g MTT assay was performed to test the cell viability of HepG2 and Hep3B cells transfected with sh-control or sh-HBXIP. After 48 h of the transfection, the gradient concentrations of sorafenib (SF) were used to treat the indicated cells. 10 μM ferrostatin-1 (a ferroptosis inhibitor, Fer-1) or DMSO along with sorafenib was added into sh-HBXIP and sh-control group. h A colony photograph of Hep3B cells transfected with sh-control or sh-HBXIP. After 48 h of the transfection, DMSO or 3 μM sorafenib was used to treat the indicated stable cells for at least 2 weeks. 10 μM Fer-1 or DMSO along with sorafenib was added into sh-HBXIP group. i, j MDA and GSH were detected in HepG2 and Hep3B cells transfected with sh-control or sh-HBXIP. After 48 h of the transfection, the gradient concentrations of sorafenib were utilized to treat the indicated cells. 10 μM Fer-1 or DMSO along with sorafenib was added into sh-HBXIP group. Columns with error bars symbolize the average of three independent replicates ± SD. Three experiments with consistent results tendency were analyzed by two-tailed Student’s t test (b–e) or two-way ANOVA (f–j). ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05, ns not significant.