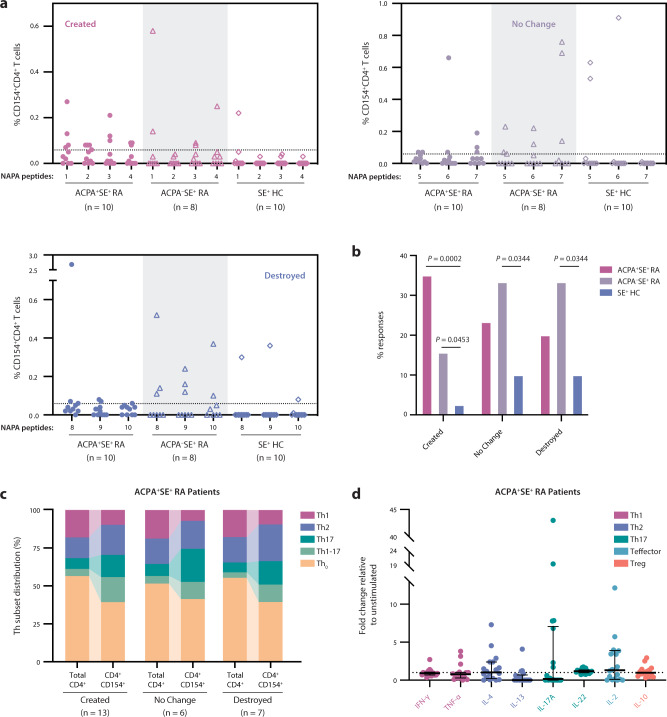
Fig. 6. Unmodified, citrullination-dependent epitopes stimulate ACPA+SE+ RA patient CD4+ T cells more robustly than native antigen–derived epitopes.
a PBMCs from ACPA+SE+ RA patients (n = 10), ACPA–SE+RA patients (n = 8), and SE+ healthy controls (n = 10) were stimulated with created peptides (1–4), no change peptides (5–7), and destroyed peptides (8–10) derived from NAPA (Fig. 5a). Percentage of CD154+CD4+ T-cell response to each peptide is shown. b Percentage of potential T-cell responses (where the number of potential T-cell responses were defined as total patients per group multiplied by the total peptides per group) is shown. Two-sided χ2 tests were used to compare the frequency of T-cell responses between patient groups. Only significant P values (≤0.05) are shown. c Distribution of ACPA+SE+ RA patient CD4+ T-helper subsets (denoted in legend) in either the total CD4+ or the CD4+CD154+ T-cell population in response to stimulation with created, no change, or destroyed peptides. d ACPA+SE+ RA patient (n = 18) PBMC cytokine secretion in response to 48-h stimulation with the created peptide pool, normalized to unstimulated samples. The dotted line at a fold change of 1 represents the normalized unstimulated values. Data are presented as median and IQR.