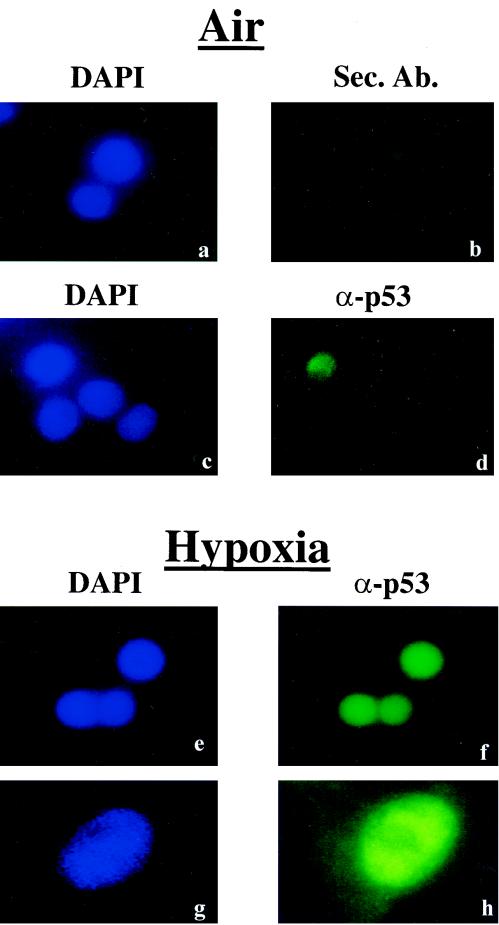
FIG. 5.
Hypoxia-induced p53 is mainly localized to the nucleus. RKO cells were grown under normoxia (a to d), or exposed to hypoxia (e to h). Nuclei were visualized with DAPI (4′,6′-diamidino-2-phenylindole) counterstaining (a, c, e, and g), while p53 was visualized using the DO-1 monoclonal antibody and a fluorescein-conjugated mouse secondary antibody (d, f, and h). Panel b depicts fluorescence due to binding of the secondary antibody alone. Images in panels g and h were taken using a higher magnification objective (×60) than the other panels (×20).