Fig. 2. In vivo efficacy of TKB245 and TKB248 against SARS-CoV-2NC928-2NOmicron_BA.1, SARS-CoV-2UW-5250Delta and SARS-CoV-2NCD1288Omicron_BA.2-infected hACE2-knocked-in mice.
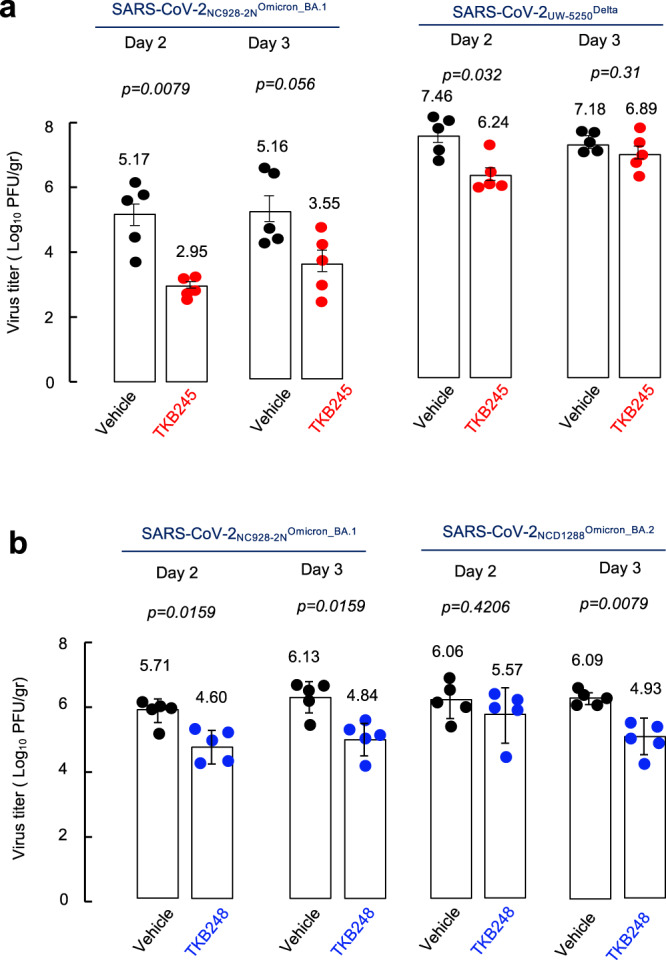
a Five hACE2KI mice per group were challenged intranasally with SARS-CoV-2NC928-2NOmicron (5 × 105 PFU) or SARS-CoV-2UW-5250Delta (5 × 105 PFU). Two hours later, animals were intraperitoneally administered 100 mg/kg BID TKB245 or vehicle (placebo). Animals were euthanized on 2- and 3-days post infection and lungs collected for determination of virus titers using VeroE6TMPRSS2 cells. Bars indicate mean values and error bars represent standard deviations. All p values are calculated using the exact Wilcoxon rank-sum test with two-sided, and no multiple adjustment was made. Source data are provided as a Source Data file. b Five hACE2K mice per group were challenged intranasally with SARS-CoV-2NC928-2NOmicron_BA.1 (5 × 105 PFU) or SARS-CoV-2NCD1288Omicron_BA.2 (1 × 105 PFU). Two hours later, animals were intraperitoneally administered 120 mg/ kg BID TKB248 or vehicle (placebo). Animals were euthanized on 2- and 3-days post infection and lungs collected for determination of virus titers using VeroE6TMPRSS2 cells. Bars indicate mean values and error bars represent standard deviations. All p values are calculated using the exact Wilcoxon rank-sum test with two-sided, and no multiple adjustment was made. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.
