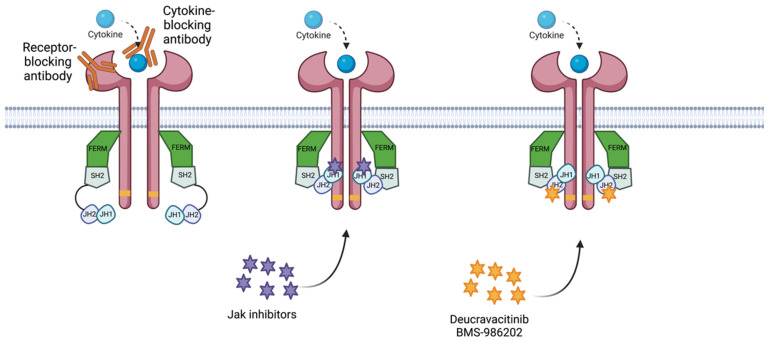
Figure 4.
Diagram of mechanism of action for the treatments for IMIDs. The receptor-blocking antibody binds to the receptor, preventing its capacity to bind to the cytokine. The. cytokine-blocking antibody binds to the cytokine, blocking its capacity to bind to the receptor. Jak inhibitors bind to the JH1 domain—kinase domain—impeding adenosine triphosphate (ATP) binding to the JH1 catalytic domain. Deucravacitinib and BMS-986202 bind to the JH2 domain, locking the regulatory (JH2) domain into an inhibitory contact with the catalytic domain (JH1). Created with BioRender.com (accessed on 14 January 2023). Abbreviations: FERM, 4.1 ezrin, radixin moesin domain; SH2, Src-homology 2 domain; JH1, jak homology domain 1 (kinase domain); JH2, jak homology domain 2 (pseudokinase domain).