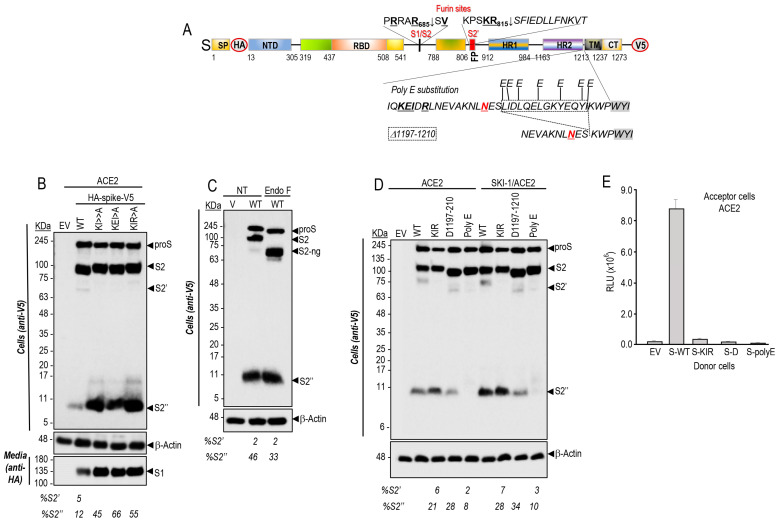
Figure 4.
Identification of a potential shedding site of spike glycoprotein. (A) Schematic representation of the primary structure of preproS showing WT sequence and the mutants of the C-terminal of HR2 domain. (B) Western blot analyses of HeLa cells following co-transfection with cDNAs coding for ACE2 and either WT-S-protein or its mutants: double KI (K1181A + I1183A) or triples KEI (K1181A + E1182A + I1183A), and KIR (K1181A + I1183A + R1185A) mutants. Note that mutants significantly enhanced the generation of S2″ accompanied by the loss of S2′. (C) Extracts from HeLa cells transfected with empty vector (EV) or V5-tagged wild type spike-protein (WT) were treated with Endo-F or mock treated (NT) and analyzed by Western blot using anti-V5 antibody. Note the molecular shift of non-N-glycosylated forms (ng) proS, S2 and S2′ but not that of S2″ fragment after endo-F treatment. (D) Western blot analysis using mAb-V5 of cell lysates from HeLa cells expressing ACE2 with empty vector (EV), wild type spike-protein (WT), or its mutants: KIR (K1181A + I1183A + R1185A), Δ-S (Δ1197-1210), or poly E substitution in the absence or presence of SKI-1. (E) Cell-to-cell fusion assay of donor HeLa cells expressing either empty vector (EV), wild type spike-protein (WT), or its mutants: KIR, Δ-S, or poly E substitution with acceptor cells expressing ACE2 receptor. All the mutants in the HR2 domain abrogate cell-to-cell fusion.