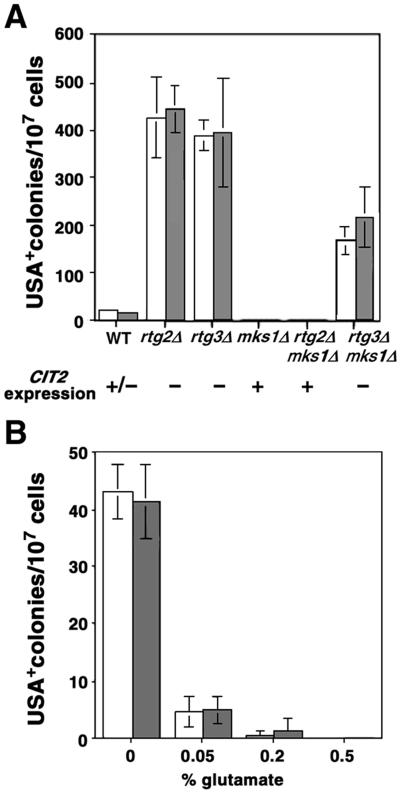
Figure 7.
Effects of rtg mutations and glutamate on [URE3] formation. Two independent colonies of an MLY42 derivative (MATα ura2) were analyzed in parallel as indicated by the unshaded and shaded bars. (A) Effects of inactivation of RTG and MKS1 on [URE3] formation. Wild-type (derived from MLY42, a Σ1278b background strain) and isogenic rtg2Δ, rtg3Δ, mks1Δ, rtg2Δ mks1Δ, and mks1Δ rtg3Δ mutant derivatives (all contain an ura2Δ::kanMX4 mutation) were grown in YPD medium for 2 d to saturation. Cells were pelleted and washed twice with sterile water. For each strain, 106 or 107 cells were plated on each of seven YNBD plates supplemented with 200 μg/ml ureidosuccinic acid and 0.01% glutamate. The number of USA+ colonies per plate was determined after 5 d of incubation at 30°C. Two independent colonies of each strain were analyzed as indicated by the shaded and unshaded bars. Error bars indicate SD of colony numbers from seven plates. CIT2 expression refers to the qualitative level of CIT2 expression in the various strains grown in YPD medium. (B) Glutamate inhibits [URE3] formation. Cells were cultured and plated in the same way as in A except that YNBD plates supplemented with 200 μg/ml ureidosuccinic acid and the indicated amounts of glutamate were used. Error bars indicate SD of colony numbers from seven plates.