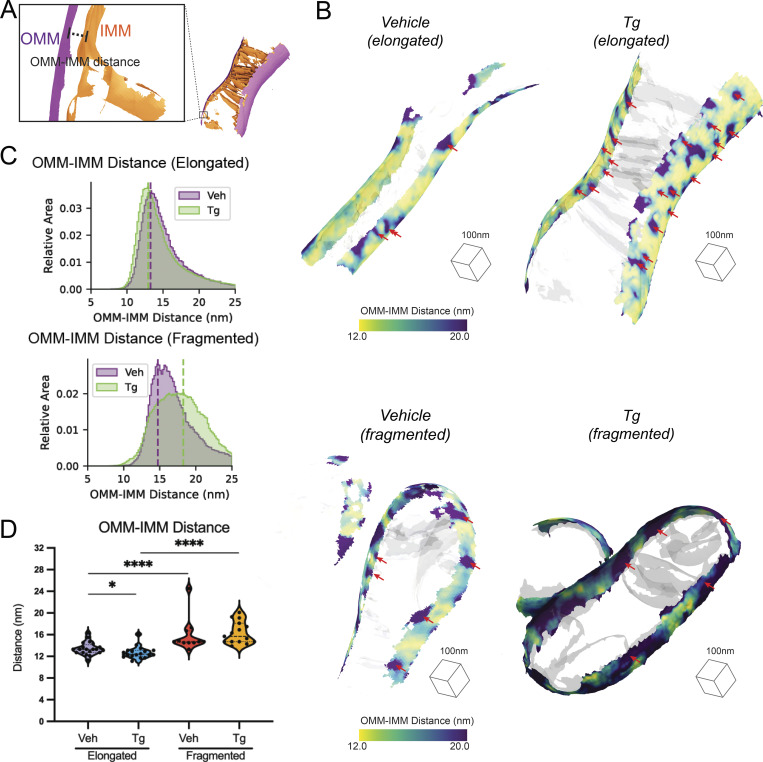
Figure 3.
Distance between IMMs and OMMs is dependent on mitochondrial network morphology and presence or absence of ER stress. (A) Surface membrane reconstruction defining OMM (purple) and IMM (orange) distance measurement. (B) Representative membrane surface reconstructions of elongated (top) and fragmented (bottom) mitochondria in MEFmtGFP cells treated with vehicle and Tg (500 nM, 8 h). The OMM surface is colored by outer-to-inner (OMM–IMM) membrane distance, and the IMM surface is shown in transparent gray. Red arrows indicate regions on OMM with large OMM–IMM distances that correspond to cristae junctions. (C) Combined histogram of OMM–IMM distances of elongated (top) and fragmented (bottom) mitochondria in MEFmtGFP cells treated with vehicle and Tg. Dashed vertical lines correspond to peak histogram values of pooled data. (D) Quantification of peak histogram values from each mitochondrion within the indicated treatment and mitochondrial morphology class. Quantifications from vehicle elongated n = 20, Tg elongated n = 18, vehicle fragmented n = 11, and Tg fragmented n = 15 mitochondria are shown. P values from Mann–Whitney U test are indicated. *P < 0.05; ****P < 0.001.