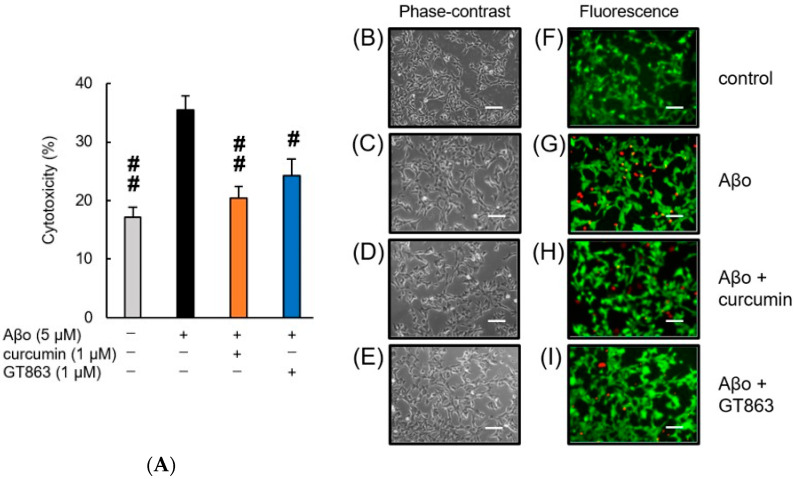
Figure 4.
Effect of curcumin and GT863 on the cytotoxicity in Aβo-stimulated SH-SY5Y cells. The cytotoxicity in Aβo-stimulated SH-SY5Y cells was evaluated using EthD-1 cell assay. (A) The cytotoxicity of SH-SY5Y cells exposed to 5 µM Aβo and treated with Aβo + 1 µM curcumin, Aβo + 1 µM GT863. +: inclusion of 5 µM Aβo, curcumin, GT863; −: non-inclusion. The p-values in ANOVA were < 0.001. Each value expresses the mean + S.E.M. of at least 3 independent experiments. In the absence of 5 µM Aβo, the cytotoxicity of control, 1 µM curcumin-treated, 1 µM GT863-treated cells were 17.15 ± 1.67, 19.23 ± 1.74, and 19.11 ± 1.41%, respectively (no significant difference, n = 10, Tukey). #, p < 0.01, ##, p < 0.0001 for Aβo-exposed cells versus the other treated cells (n = 10, Tukey). (B–I) SH-SY5Y cells stained with calcein AM and Ethdium homodimer-1 observed using phase-contrast (B–E) and fluorescence microscopy (F–I). (B,F) Untreated SH-SY5Y cells; (C,G) SH-SY5Y cells exposed to 5 µM Aβo; (D,H) SH-SY5Y cells treated with 5 µM Aβo + 1 µM curcumin; (E,I) SH-SY5Y cells treated with 5 µM Aβo + 1 µM GT863. The scale bars represent 100 µm.