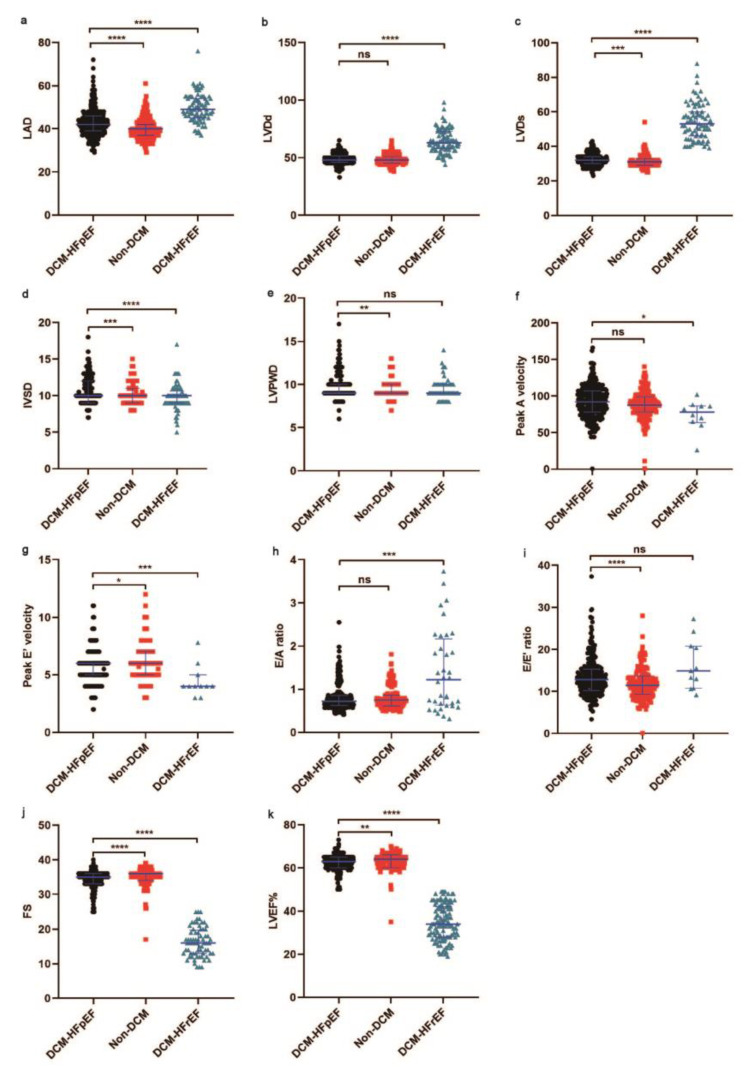
Figure 3.
Comparison of echocardiography data during hospitalization of DCM-HFpEF vs. non-DCM and DCM-HFpEF vs. DCM-HFrEF. (a) LAD was higher in DCM-HFrEF vs. DCM-HFpEF and lower in non-DCM vs. DCM-HFpEF. (b,c) LVDd and LVDs were higher in DCM-HFrEF vs. DCM-HFpEF. (d) IVSD was higher in DCM-HFpEF vs. non-DCM and DCM-HFrEF. (e) LVPWD was higher in DCM-HFpEF vs. non-DCM. (f) Peak A velocity was higher in DCM-HFpEF vs. DCM-HFrEF. (g) Peak E’ velocity was higher in non-DCM vs. DCM-HFpEF and lower in DCM-HFrEF vs. DCM-HFpEF. (h) E/A ratio was higher in DCM-HFrEF vs. DCM-HFpEF. (i) E/E’ was lower in non-DCM vs. DCM-HFpEF. (j) FS was higher in non-DCM vs. DCM-HFpEF and lower in DCM-HFrEF vs. DCM-HFpEF. (k) LVEF% was higher in non-DCM vs. DCM-HFpEF and lower in DCM-HFrEF vs. DCM-HFpEF. LVEF: left ventricular ejection fraction; LAD: left atrial diameter; IVSD: ventricular septum diameter; LVPWD: left ventricular posterior wall diameter; LVDd: left ventricular diameter in diastole; LVDs: left ventricular diameter in systole; FS: fractional shortening; Peak A velocity: the maximum early transmitral flow velocity in atrial systole; Peak E velocity: the maximum early transmitral flow velocity; E/A ratio: the ratio of the early (E) to late (A) ventricular filling velocities; E/E’ ratio: the ratio of mitral peak velocity of the early filling (E) to early diastolic mitral annular velocity (E). DCM: diabetic cardiomyopathy; HFrEF: heart failure with reduced ejection fraction; HFpEF: heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Black represents DCM-HFpEF, red represents non-DCM, green represents DCM-HFrEF. * p < 0.05. ** p < 0.01. *** p < 0.005. **** p < 0.001.