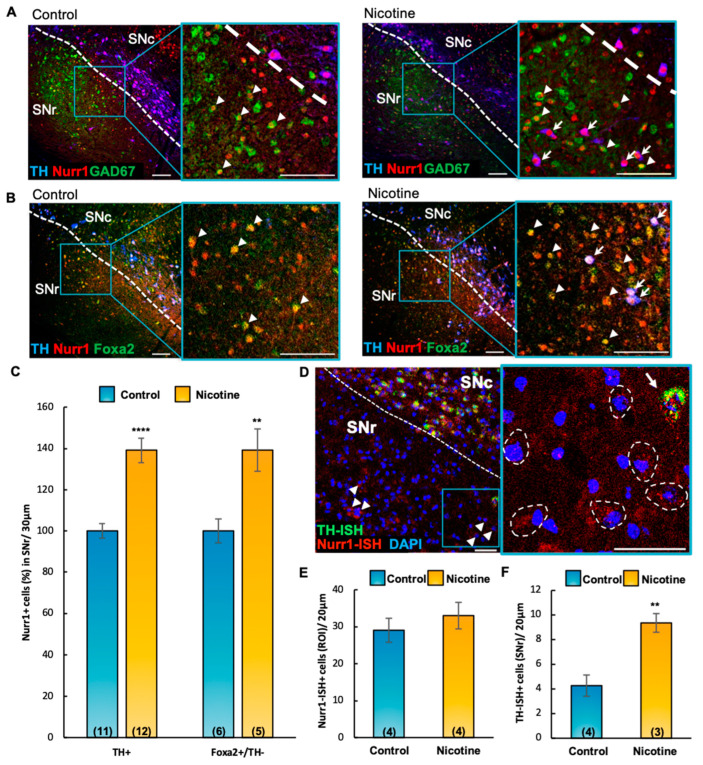
Figure 4.
Chronic nicotine exposure increases Nurr1 expression via translational upregulation and induces de novo transcription of TH in non-DAergic cells. (A,B) Confocal images of coronal sections (30 μm) through the SN of control (left panels) and nicotine-exposed (right panels) mice, labeled with TH, Nurr1, GAD67-GFP, and Foxa2 markers. Insets display immunoreactive TH-/Nurr1+/GAD67+ ((A), arrowheads), TH-/Nurr1+/Foxa2+ ((B), arrowheads) cells in the SNr. Scale bars = 100 μm. (C) Quantification (%) of IHC preparations shown in (A,B) indicated that chronic nicotine exposure in adult (P60) mice increased the number of TH+/Nurr1+ (t(21) = 5.51, p < 0.0001) and TH-/Foxa2+/Nurr1+ (t(9) = 3.50, p < 0.01) cells in the SNr (arrows in A,B). Graph shows mean ± SEM: ** p < 0.01, **** p < 0.0001. (D) Confocal image of Nurr1/TH in situ hybridization (ISH) of a representative coronal section (20 μm) through the SN of nicotine-exposed adult (P150) mice. DAPI was used to label nuclei. Non-DAergic (TH-ISH negative) Nurr1-ISH+ cells (arrowheads, dashed contours in inset) and TH-ISH+/Nurr1-ISH+ cell (arrow) are observed in the SNr. Scale bars = 50 μm. (E,F) Quantification of ISH preparations shown in D (ROI, 200 μm × 200 μm) revealed no difference in the number of Nurr1-ISH+ cells between control and nicotine-exposed groups (E). Chronic nicotine exposure increased the number of TH-ISH+ cells ((F), t(5) = 4.06, p < 0.01). Graphs show mean ± SEM: ** p < 0.01. The number of animals is annotated in parentheses for each condition. ROI, Region of Interest; SNc and SNr, substantia nigra compacta and reticulata. Graphs show mean ± SEM: ** p < 0.01. The number of animals is annotated in parentheses for each condition.