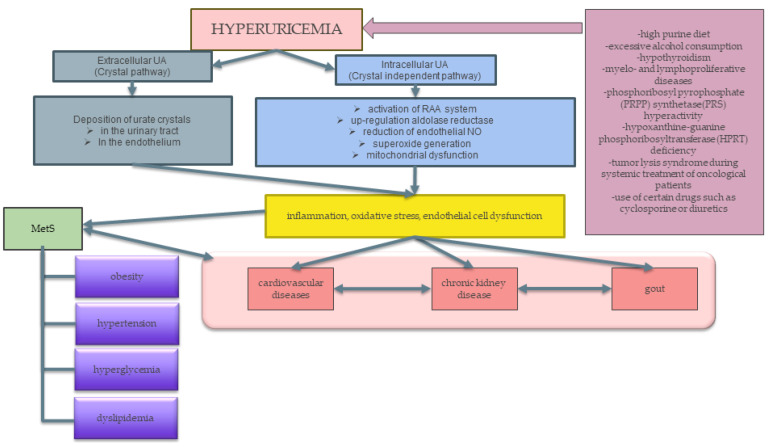
Figure 1.
The relationship between hyperuricemia and MetS. Factors such as a high purine diet, high alcohol consumption, certain diseases, consumption of certain drugs, or metabolic disorders lead to an increase in the level of uric acid in the blood, which then causes an increase in inflammation, oxidative stress, and epithelial cell dysfunction. This leads to the development of MetS-related illnesses and diseases, gout, cardiovascular disease, and chronic nephritis. Abbreviations: MetS—metabolic syndrome; RAA—renin–angiotensin–aldosterone; NO—nitric oxide.