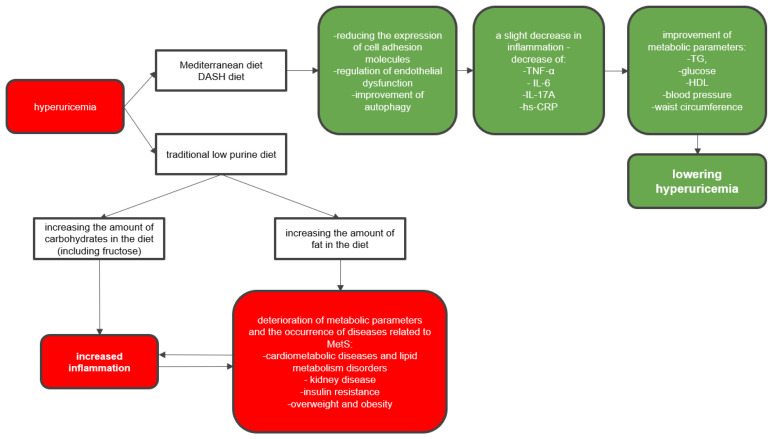
Figure 4.
Consequences of improper dietary interventions in patients with hyperuricemia and MetS-related diseases. Following a low-purine diet leads to supplementation of calories with carbohydrates and fats, which may exacerbate MetS-related conditions. The use of an otherwise balanced diet (Mediterranean, DASH) may alleviate the symptoms of MetS and reduce hyperuricemia. Abbreviations: TG—triglycerides; HDL—high density lipoprotein; MetS—metabolic syndrome; TNF-α—tumor necrosis factor α; IL-6—interleukin 6; IL-17A—interleukin 17A; hs-CRP—high sensitivity C-reactive protein; DASH—Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension diet.