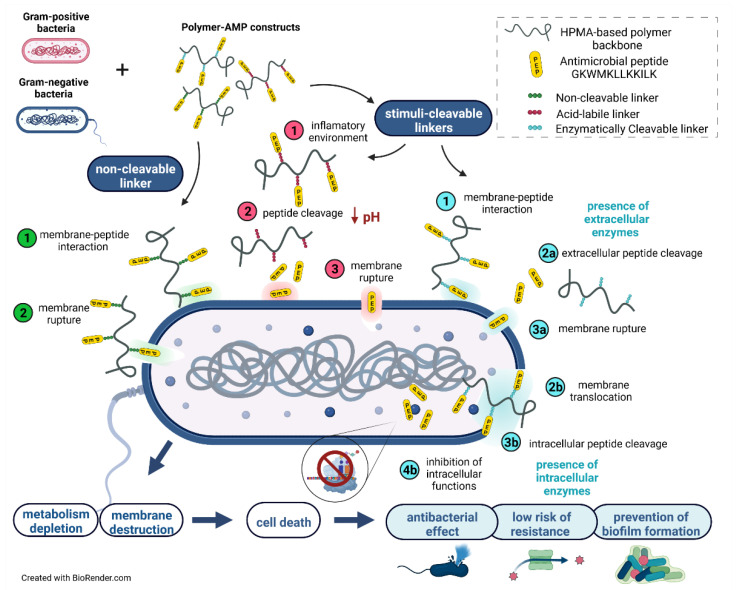
Figure 2.
The proposed mechanism of the polymer-antimicrobial peptide construct action. Green—“polymer-bound PEP caused the rupture of bacterial membrane”—the bacterial membrane is disrupted by the polymer-bound AMP. Red—“released PEP caused the rupture of bacterial membrane”—pH-responsive extracellular release of the AMP followed by membrane interaction of low-molecular-weight AMP. Blue—“enzymatically-triggered PEPs’ release and action”—the mechanism is divided into: (i) the enzymatic AMP release caused by extracellular membrane-enzymes, and (ii) polymer-bound AMP penetration of the bacterial membrane, followed by enzymatically triggered cleavage that causes inhibition of various intracellular functions. Figure was created with Biorender.com.