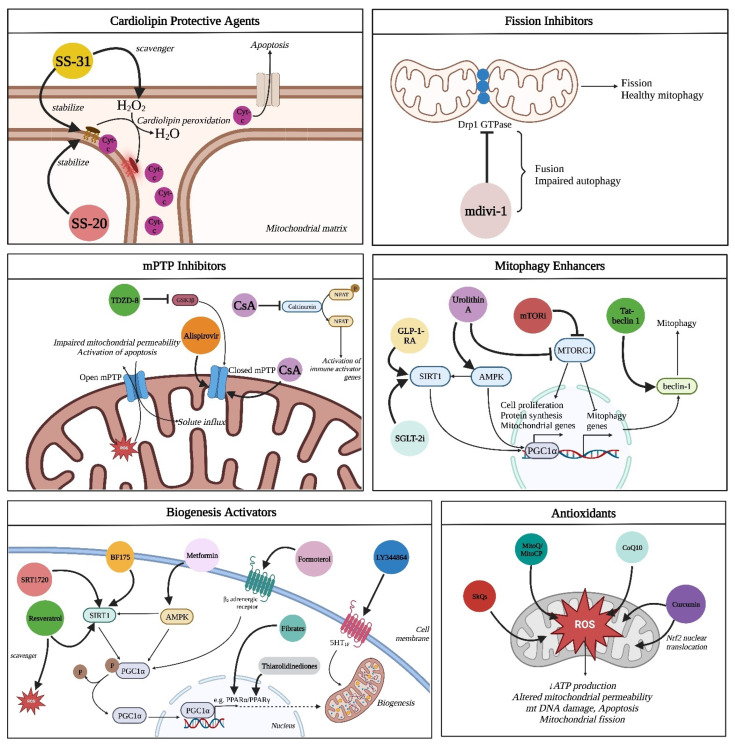
Figure 3.
Mechanism of actions of mitochondria-targeting drugs that are used in kidney diseases. cyt-c: cytochrome c, SS-31: Szeto–Schiller peptide 31, SS-20: Szeto–Schiller peptide 20, DRP1 GTPase: dynamin-related protein 1 guanosine triphosphatase, mdivi-1: mitochondrial division inhibitor 1, GSK3b: glycogen synthase kinase 3beta, NFAT: nuclear factor of activated T-cells, ROS: reactive oxygen species, mPTP: mitochondrial permeability transition pore, CsA: cyclosporine A, SIRT1: Sirtuin1, AMPK: AMP-activated protein kinase, MTORC1: mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1, PGC1a: peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator-1a, mTORi: mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor, PPARa: peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha, 5HT1F: 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 1F, SkQs: plastoquinone, CoQ10: coenzyme Q10, Nrf2: the nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2, ATP: adenosine triphosphate, mtDNA: mitochondrial DNA, GLP-1-RA: glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists, SGLT-2i: sodium glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors. Downward arrow indicates “decrease”.