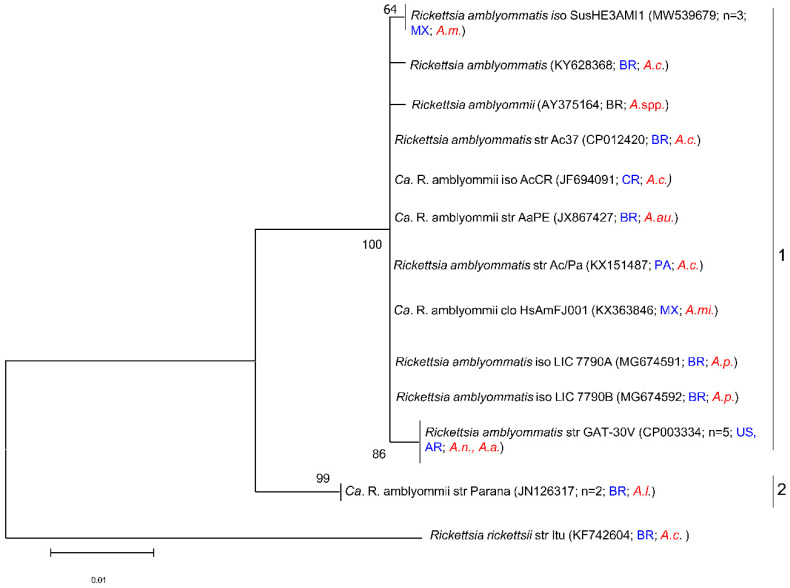
Figure 4.
Phylogenetic tree of published sequences and reports of Rickettsia amblyommatis in ticks. The analyses were based on 20 partial sequences of the ompB gene region of Rickettsia amblyommatis within 618 bp obtained from NCBI BLAST. The phylogenetic analysis was completed using a maximum likelihood method on the Kimura 2-parameter model (ML; bootstrap replicates: 1000). This tree is collapsed with nodes organized by sequence differences of 0.001 (n shows the total number of sequences included in that group). Instances in which papers reported the species as “Rickettsia spp.” but indicated in the publication that the species was R. amblyommatis were included in this analysis. The GenBank accession numbers are given in parentheses. Scale bars indicate the number of substitutions per nucleotide position. This phylogenetic tree was created using MEGA11. Tick species included in this tree are as follows: A. americanum (A.a.), A auricularium (A.au.), A. cajennense (A.c.), A. longirostre (A.l.), A. maculatum (A.m.), A. mixtum (A.mi.), A. neumanni (A.n.), A. pseudoconcolor (A.p.), and Amblyomma spp. (A.spp.). The countries included in this tree are as follows: Brazil (BR), the United States of America (US), Panama (PA), Argentina (AR), Mexico (MX), and Costa Rica (CR).