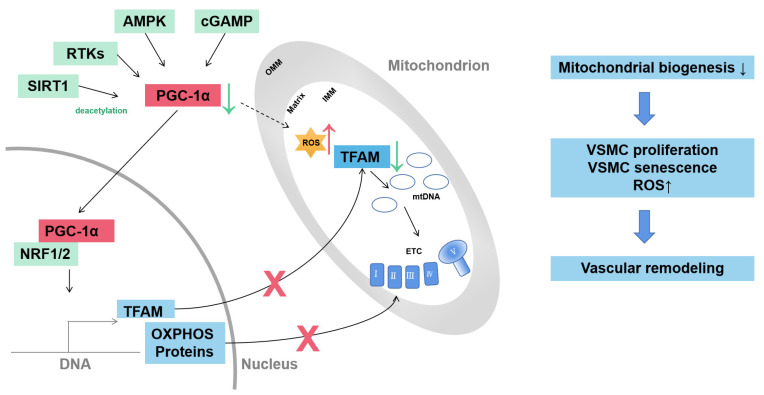
Figure 1.
Mitochondrial biogenesis of VSMC in vascular remodeling. Mitochondrial biogenesis is driven by transcriptional coactivator PGC-1α. The expression and activity of PGC-1α are regulated through diverse pathways, including RTKs, cGMP, AMPK and SIRT1. PGC-1α activates transcriptional factors NRF1 and NRF2 to induce transcription of TFAM and nDNA-encoded OXPHOS proteins. TFAM controls the transcription and replication of mtDNA. Decreased PGC-1α contributes to VSMC proliferation, senescence and ROS production and drives vascular remodeling. AMPK, adenosine monophosphate-activated kinase; cGMP, cyclic guanosine monophosphate; ETC, electron transport complex; IMM, inner mitochondrial membrane, mtDNA, mitochondrial DNA; NRF1/2, nuclear respiratory factor-1/2; OMM, outer mitochondrial membrane; OXPHOS, oxidative phosphorylation; RTKs, receptor tyrosine kinases; SIRT1, sirtuin 1; TFAM, mitochondrial transcription factor A; VSMC, vascular smooth muscle cell.