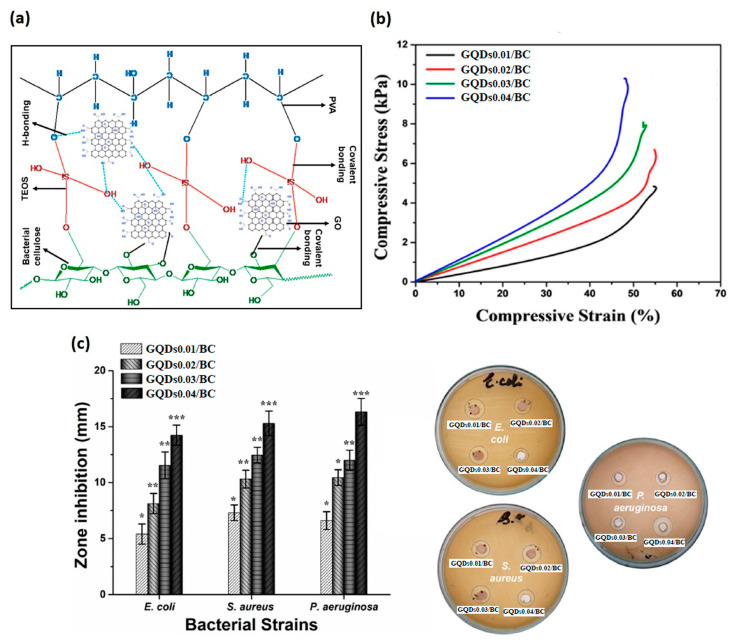
Figure 9.
(a) The proposed chemical interaction of the bacterial cellulose, polyvinyl alcohol, GO, and crosslinked via TEO; (b) stress–strain curve of hydrogels; (c) the antibacterial activities of composite hydrogels against different severe skin infections causing Gram+ and Gram− pathogens. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 and *** p < 0.00. (GQDs0.01/BC, GQDs0.02/BC, GQDs0.03/BC, and GQDs0.04/BC) were assigned to these composite hydrogels after a different GO amount (0.01, 0.02, 0.03, and 0.04 mg). Adapted from [3]. Copyright © 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland.