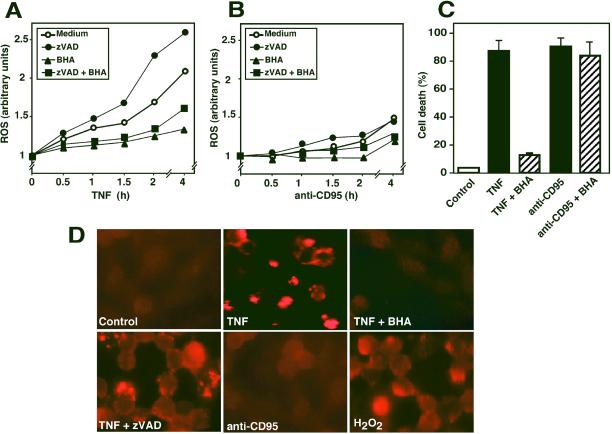
Figure 5.
Involvement of ROS formation in death receptor-induced PARP activation. (A and B) Effect of TNF and anti-CD95 on ROS formation. L929 cells were triggered with TNF (A, 40 ng/ml) or anti-CD95 (B, 1 μg/ml) for the indicated time. The antioxidant BHA (150 μM) and zVAD (50 μM) were added 15 min before treatment with the death stimuli. ROS production was measured with the dye DFCH and flow cytometry. Similar data were obtained using rhodamine-123. SDs in the above experiments were <12%. (C) Different effect of BHA on TNF- and anti-CD95–induced cell death. Cells were stimulated as described in (A) with TNF or anti-CD95 in the presence or absence of 150 μM BHA. Cell death was determined after 5 h by measurement of PI uptake. (D) Visualization of PARP activity by immunodetection of poly(ADP-ribose) chains. Cells were either stimulated with TNF (40 ng/ml) in the presence and absence of BHA or zVAD or incubated with 1 μg/ml anti-CD95 or 2 mM H2O2. PARP activation was detected with a antibody specific for poly(ADP-ribose) polymers. Note the similarity of TNF-induced and zVAD-potentiated PARP activity with the immunocytochemical signal obtained after H2O2 treatment.