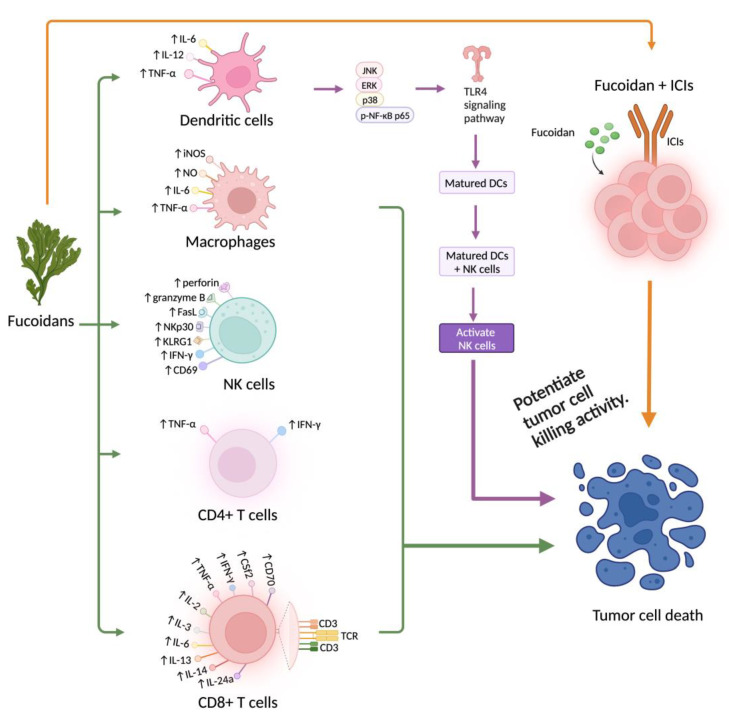
Figure 2.
Immunopotentiation and antitumor immunity of fucoidan. Fucoidan activates DC maturation via secreting IL-6, IL-12, and TNF-α; matured DCs will then activate NK cells to induce antitumor immunity effects in tumor cells. Fucoidan can activate macrophages via increasing the production of iNOS, NO, IL-6, and TNF-α. Fucoidan increases NK cell proliferation by increasing CD69 expression and IFN-γ levels and activates NK cells by upregulating the cytotoxic mediators of perforin, granzyme B, activating the receptor NKp30, FasL, and KLRG1. Here, TNF-α and IFN-γ are the two common cytokines expressed on the surface of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. Fucoidan activates these T cells via upregulating cytokines of TNF-α, IFN-γ, CD70, CSf2, IL-2, IL-3, IL-6, IL-13, IL-14, IL-24a, to induce tumor cell death. Fucoidan is co-administered with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) to enhance tumoricidal activity (this figure was created with BioRender.com, accessed on 5 February 2023).