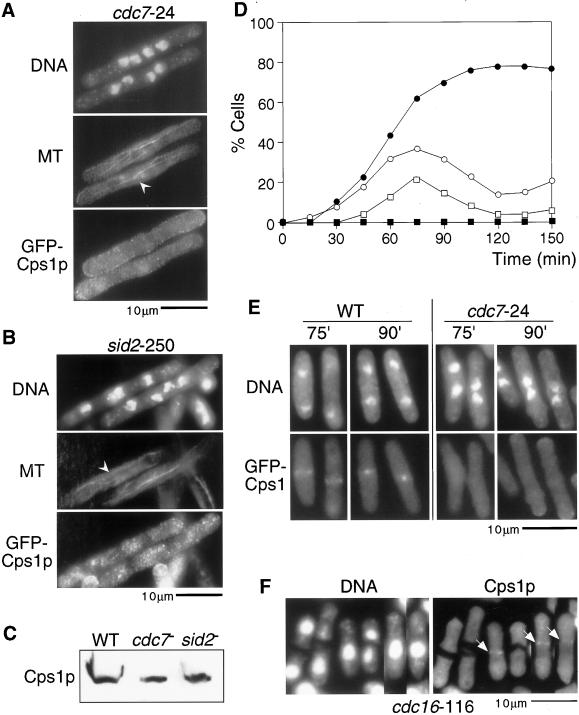
Figure 9.
The SIN proteins are essential for Cps1p assembly to the division site. GFP-Cps1p cells bearing either a cdc7-24 allele (A) or a sid2-250 (B) were grown at nonpermissive temperature (36°C) and stained for DNA, microtubules (MT), and GFP-Cps1p with DAPI, TAT1 antibodies, and anti-GFP antibodies. Arrowheads indicate cells with postanaphase-like microtubular arrangement. (C) Lysates from wild-type, cdc7-24, and sid2-250 cells were fractionated in SDS-PAGE gels and immunoblotted with anti-Cps1p antibodies. (D) Plot shows the percentage of cells containing two nuclei (○, ●), and GFP-Cps1p medial ring structures (□, ▪) in lactose gradient-synchronized wild-type cells (○, □) or cdc7-24 mutant cells (●, ▪) expressing GFP-Cps1p. (E) Images of lactose gradient-synchronized wild-type and cdc7-24 mutant cells expressing GFP-Cps1p. Although wild-type cells assembled a peak of GFP-Cps1p rings at 75–90 min after shift-up, no GFP-Cps1p rings were detected in cdc7-24 mutant cells after shift-up. (F) Cells bearing the cdc16-116 allele were grown at nonpermissive temperature and stained for DNA and Cps1 with DAPI and affinity-purified anti-Cps1p antibodies, respectively. Arrows indicate Cps1p rings.