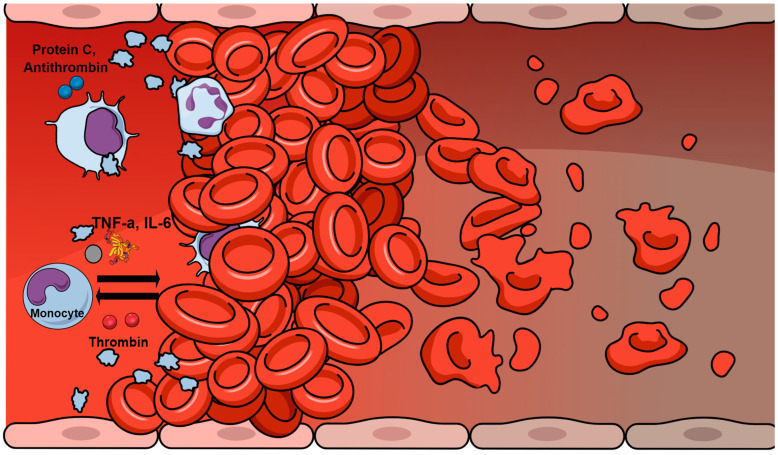
Figure 3.
Main mechanisms involved in hemostasis–inflammation cross talk. Pro-inflammatory mediators such as tumor necrosis factor-a (TNF-a) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) are released by monocytes and macrophages to induce the coagulation cascade, while transmembrane receptors on monocytes can be activated by thrombin and other coagulation factors to trigger the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Moreover, antithrombin can directly bind to inflammatory cells and suppresses the expression of cytokine receptors, while also activated protein C downregulates endotoxin-induced production of cytokines by monocytes and macrophages.