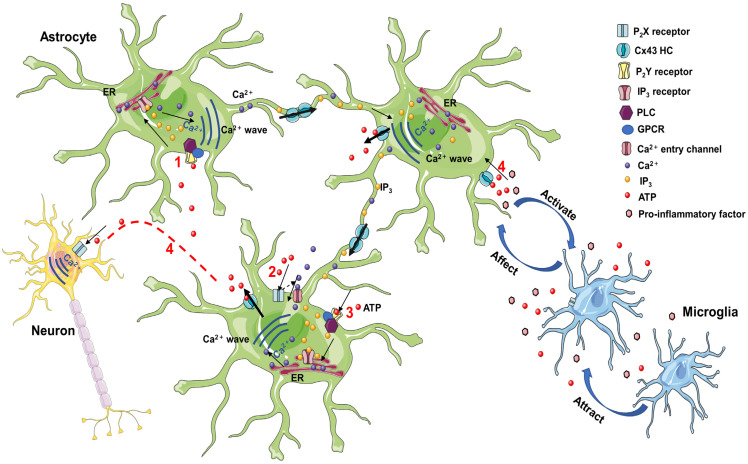
Figure 2.
(1) Extracellular ATP stimulation to the activation of PLC and the formation of IP3, which, upon binding to ER receptors, promotes the release of Ca2+ stored in the ER. IP3 and Ca2+ diffuse to adjacent cells through GJC, resulting in the diffusion of intracellular Ca2+ waves. (2) Extracellular ATP leads to the entry of extracellular Ca2+ into the cell by activating membrane P2X receptors. (3) Activation of P2Y receptors by ATP leads to PLC activation and IP3 formation. Increased Ca2+ waves are induced by IP3 and P2X receptor opening, promoting ATP release through Cx43 HC, and extending Ca2+ waves to neighboring cells. (4) Astrocyte ATP release induces intraneuronal Ca2+ waves. Astrocyte HCs release ATP into the extracellular space, creating an ATP concentration gradient that triggers microglia activation. Extracellular ATP induces the microglia to release endogenous ATP that attracts distant microglia and promotes the inflammatory cascade. ATP, adenosine triphosphate; PLC, phospholipase C; IP3, 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; GPCR, G-protein-coupled receptors; GJC, gap junction channel; HC, hemichannel.