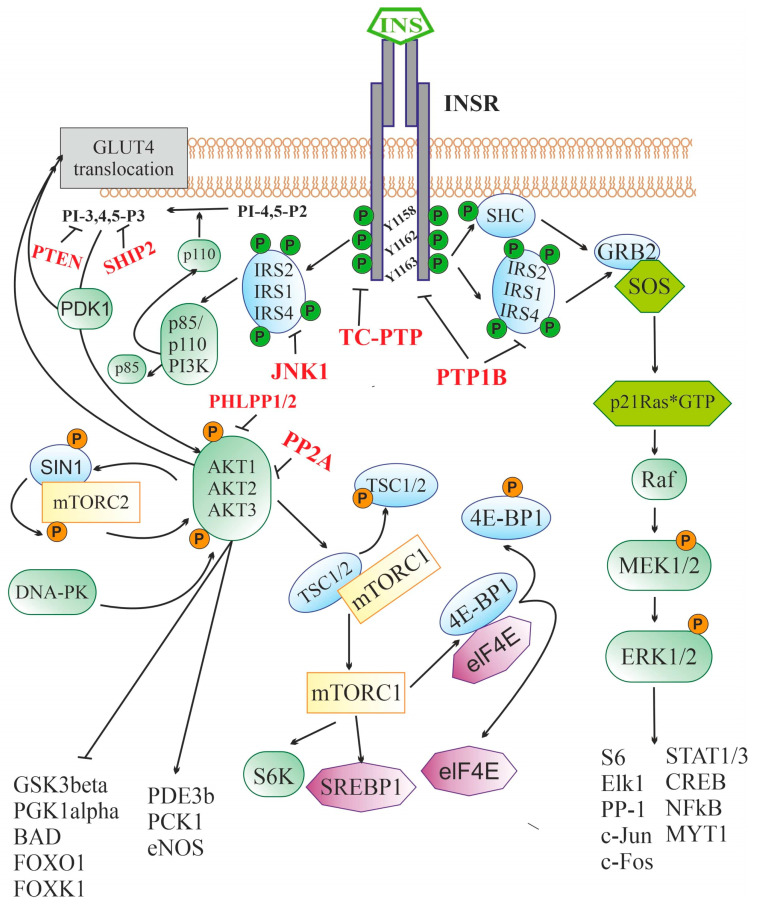
Figure 1.
Insulin-activated signaling pathways. Abbreviations: INSR—insulin receptor, containing three sites for tyrosine phosphorylation (Y1158, Y1162, and Y1163); IRS1, IRS2, and IRS4—insulin receptor substrates-1, -2 and -4, respectively; p85 and p110 PI3K—p85-regulatory and p110-catalytic subunits of phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase; PI-4,5-P2—phosphatidylinositol-4,5-diphosphate; PI-3,4,5-P3—phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-triphosphate; PDK1—phosphoinositol-dependent protein kinase-1; AKT1, AKT2, and AKT3—serine/threonine-specific protein kinase B (AKT kinase) of the types 1, 2 and 3, respectively; DNA-PK—DNA-dependent protein kinase; mTORC2—mammalian target of rapamycin complex 2 that includes the protein kinase mTOR, the regulatory protein RICTOR (Companion of mammalian Target Of Rapamycin), mSIN1 protein (mammalian Stress-activated protein kinase Interacting Protein 1) and some other components; GLUT4—type 4 insulin-dependent glucose transporter; GSK3beta—glycogen synthase kinase-3β; PGK1alpha—peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator 1α; BAD—BCL2 antagonist in cell death; FOXO1 and FOXK1—transcription factors of FOX (forkhead box) family; PDE3B—subtype 3B cAMP-dependent phosphodiesterase; PCK1—phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase 1; eNOS—endothelial isoform of NO synthase; mTORC1—mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1; TSC1/2—tuberous sclerosis proteins 1 (hamartin) and 2 (tuberin); S6K—p70 ribosomal S6 kinase; SREBP1—Sterol regulatory element-binding transcription factor 1; eIF-4E—eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E; 4E-BP1—eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E-binding protein 1; SHC—adapter SH2/α-collagen-like protein; GRB2—adapter protein-2 associated with growth factor receptors; SOS—metabolic protein (Son of Sevenless), induced GDP/GTP exchange; p21Ras*GTP—small GTP-binding protein of the Ras family in GTP-bound form; Raf—serine/threonine-specific protein kinase; MEK1/2—mitogen-activated protein kinase kinases-1 and -2; ERK1/2—mitogen-activated protein kinases-1 and -2; Elk-1—transcription factor containing the ETS (E26 transformation-specific) domain; STAT1/3—types 1 and 3 signal transducers and transcription activators; CREB—cAMP-dependent transcription factor; S6—ribosomal protein S6; NF-κB—nuclear factor κ-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; MYT1—myelin transcription factor 1; c-Fos and c-Jun—the transcription factors of the Fos and Jun families, respectively; PP-1—protein phosphatase 1; PTEN—phosphatase (Phosphatase and TENsin homolog) hydrolyzing PI-3,4,5-P3 to PI-4,5-P2; SHIP-2—SH2 domain-containing inositol-5’-phosphatase 2 hydrolyzing PI-3,4,5-P3 to PI-3,4-P2; JNK1—c-Jun N-terminal kinase-1; PP2A—protein phosphatase 2A subtype; PHLPP1/2—plekstrin-homologous (PH)-domain leucine-rich-repeat-containing protein phosphatases; PTP1B—protein phosphotyrosine phosphatase 1B; TC-PTP—T-cell protein phosphotyrosine phosphatase.