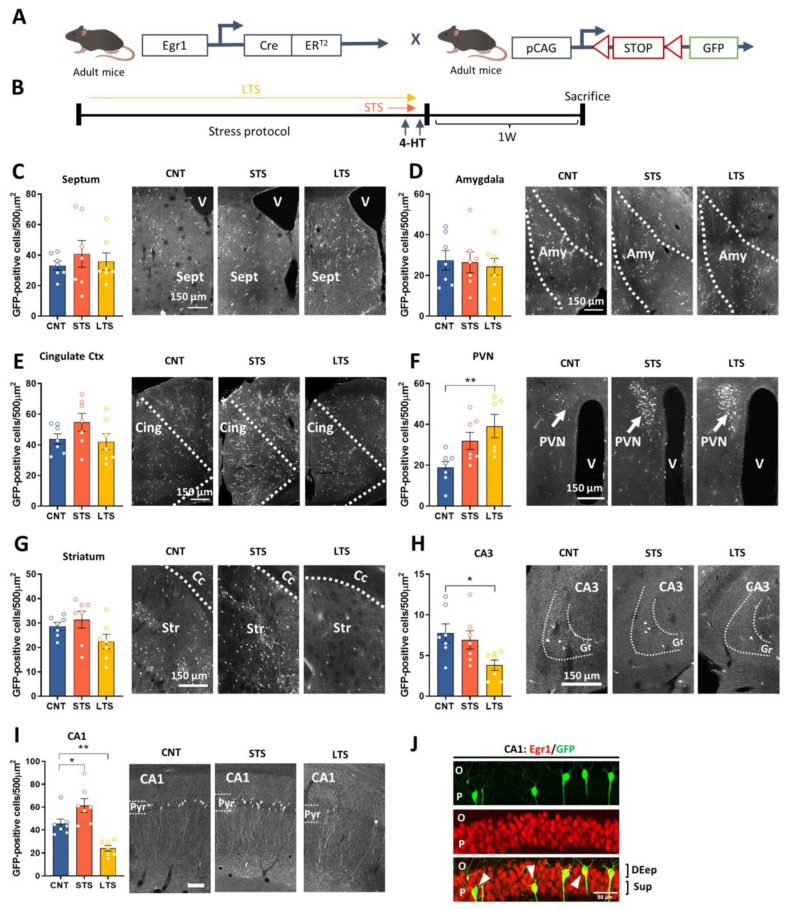
Figure 1.
Egr1-dependent activated neuronal ensembles in different brain regions by chronic stress. (A), Schematic representation of double-heterozygous-mutant Egr1-CreERT2 × R26RCE GFP mice. (B), Egr1-CreERT2 × R26RCE mice were subjected to 0 (CNT), 2 (STS) or 28 (LTS) days of CUMS. For the last two days of the protocol, all mice received 50 mg/kg of 4-hydroxytamoxifen (4-HT, i.p), and one week later they were sacrificed. Representative images and quantification of Egr1-dependent activated cells (estimated number of GFP-positive cells/area of 500 µm2) per region in: the septum (C), one-way ANOVA group effect: F(2,18) = 0.3858, p = 0.6854; the amygdala (D), group effect: F(2,18) = 0.1160, p = 0.8911; the cingulate cortex (E), group effect: F(2,18) = 1.946, p = 0.1718; the paraventricular nucleus (PVN) (F), group effect: F(2,17) = 5.686, p = 0.0129; the striatum (G), group effect: F(2,18) = 2.716, p = 0.0931; the CA3 (H), group effect: F(2,18) = 4.322, p = 0.0293, and the CA1 (I), group effect: F(2,18) = 17.63, p < 0.0001; Scale bar, 50 µm. The values are expressed as the mean ± SEM, N = 7 adult mice per condition. Dunnet’s post hoc test, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.005 compared with CNT. (J) Representative images of the CA1 of the hippocampus showing GFP-activated cells (green) and Egr1-positive cells (red). White arrows indicate double-Egr1-positive and GFP-positive cells. V, ventricle; CC, corpus callosum; O, Stratum oriens; P, Stratum pyramidale.