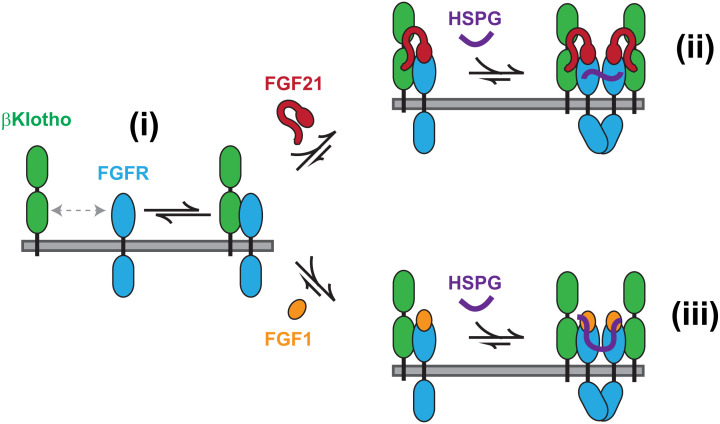
Fig. 5.
Mechanism of FGF21 and FGF1 signaling in cells with βKlotho. βKlotho–FGFR1c heterodimers in equilibrium with βKlotho and FGFR1c monomers (i) mediate the formation of FGF21–βKlotho–FGFR1c ternary complexes which are activated by HSPG-dependent dimerization of FGFR1c, with HSPG serving as a coligand for FGFR1c (ii). The same βKlotho–FGFR1c heterodimers cause βKlotho to join FGF1–FGFR1c complexes in canonical FGF1 signaling, resulting in the downregulation of βKlotho by HSPG-dependent dimerization and activation of FGFR1c, with HSPG serving as both a coreceptor for FGF1 and coligand for FGFR1c (iii). For clarity, only the heparan sulfate chain of HSPGs is depicted.