Table 1.
Chelators (including their respective derivatives) and their most suitable radiometal counterparts commonly used in biomedical applications [29]. (CA: Coordinating Atoms; CN: Coordination Number).
| Name | Chemical Structures | CA | CN | Radiometals |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DFO; desferrioxamine B |
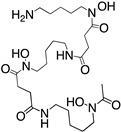
|
O6 | 6 | 89Zr4+ |
| DTPA; diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid |
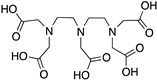
|
N3O5 | 8 | 111In3+, 177Lu3+, 86/90Y3+ |
| Pa Family; H2dedpa; 1,2-[[6-(carboxy)-pyridin-2-yl]- methylamino]ethane |
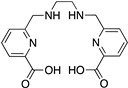
|
N4O2 | 6 | 67/68Ga3+,111In3+, 177Lu3+ |
| HOPO; 3,4,3-(LI-1,2-HOPO) |
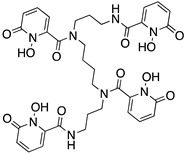
|
O8 | 8 | 89Zr4+, 227Th4+ |
| NOTA; 1,4,7-triazacyclononane-1,4,7- triacetic acid |
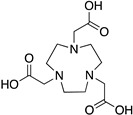
|
N3O3 | 6 | 177Lu3+, 64Cu2+, 67/68Ga3+, 86/90Y3+, 212/213Bi3+ |
| DOTA; 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane- 1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid, maximum |
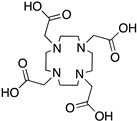
|
N4O4 | 8 | 64Cu2+, 212Pb2+, 212/213Bi3+, 177Lu3+, 225Ac3+, 111In3+, 44/47Sc3+, 86/90Y3+ |
