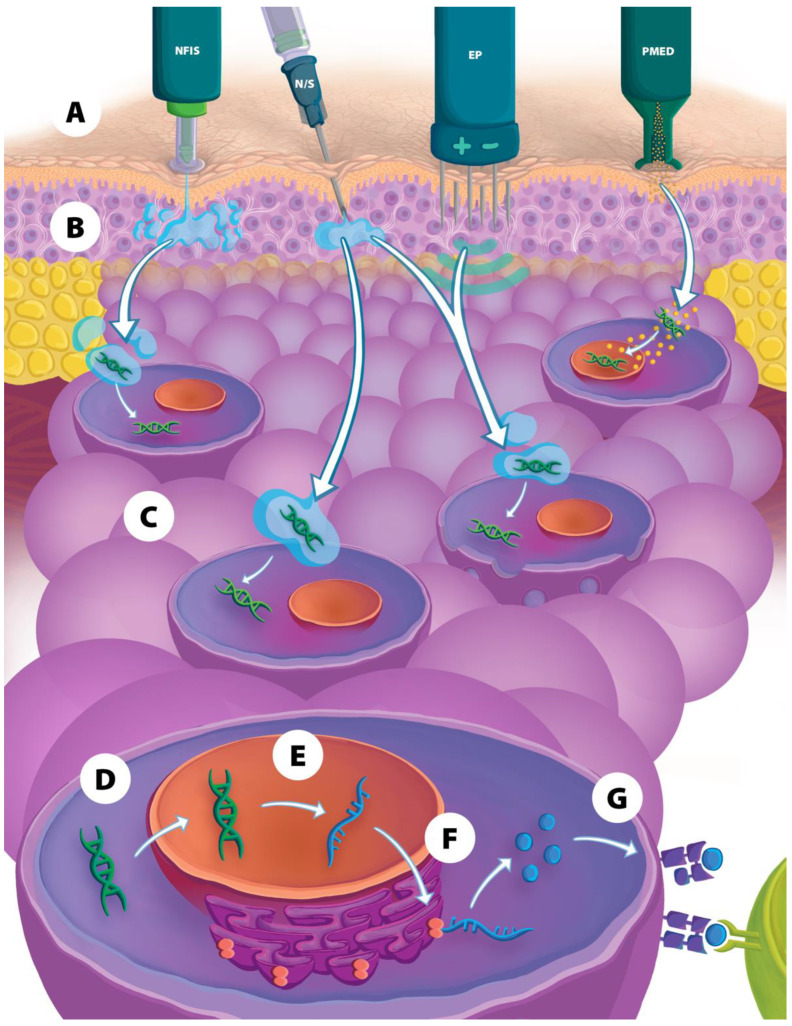
Figure 1.
Overview of physical delivery methods used for DNA vaccines. (A) Depiction of four types of physical delivery methods. (B) During injection, the DNA vaccine is inserted into either the intradermal, subcutaneous, or intramuscular tissue layer, (C) then DNA is transported into the cell, (D) and into the nucleus, (E) where the DNA is transcribed to mRNA, (F) then translated in the cytoplasm into antigenic peptides that are processed and (G) presented on the cellular surface to various immune cells for the induction of a humoral and cellular immune response. NFIS = needle-free injection system; N/S = needle and syringe; EP = electroporation; PMED = particle-mediated epidermal delivery.