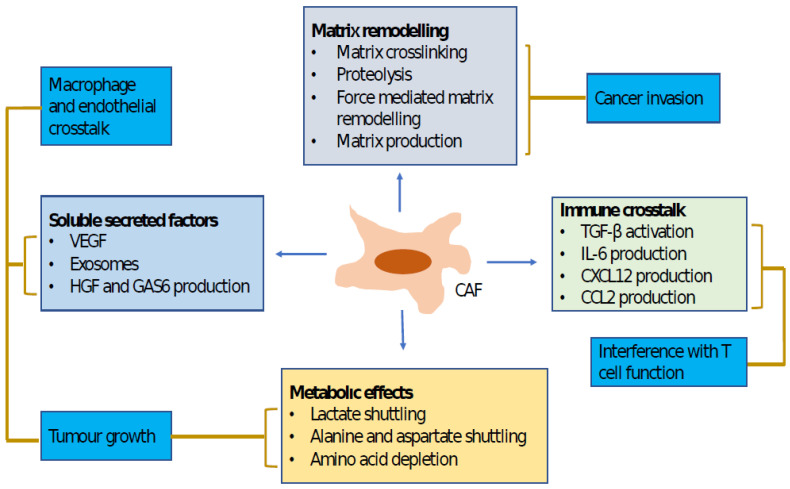
Figure 4.
This figure indicates cancer-associated fibroblast functions and the mechanisms that regulate them. Lines connect mechanisms to functions. Both matrix remodeling and production of soluble factors promote tumor-cell invasion. Soluble factors also play a critical role in tumor-cell growth and changes in tumor microenvironments, which are also influenced by the altered metabolic states of tumors. CAF, cancer-associated fibroblast; CCL2, CC-chemokine ligand 2; CXCL12, CXC-chemokine ligand 12; IL-6, interleukin 6; GAS6, growth arrest-specific protein 6; HGF, hepatocyte growth factor; TGFβ, transforming growth factor-β; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.