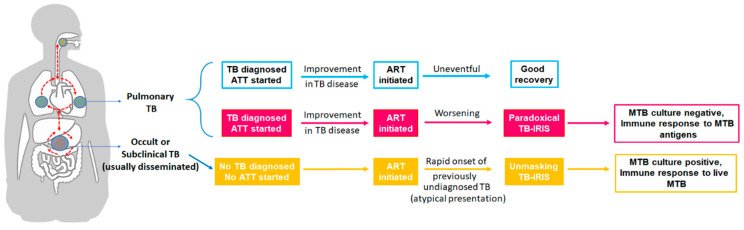
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of HIV/TB-immune reconstitution inflammatory disease. Following the initiation of anti-retroviral treatment (ART), some individuals with HIV and active TB disease display strong immune activation resulting in new or recurrent TB symptoms referred to as paradoxical TB-IRIS [11,32]. Paradoxical TB-IRIS usually develops during the first four weeks of ART and results in the flaring up of TB symptoms such as a new infiltrate, serous effusions, worsening of existing lesions, and soft tissue abscesses [33]. Unmasking TB-IRIS represents a subcategory of ART-associated TB observed in patients with undiagnosed or subclinical TB before initiation of ART. In unmasking TB-IRIS, a subclinical TB infection remains undiagnosed until ART-induced immune reconstitution elicits an exaggerated presentation of the disease [35,36]. Unmasking TB-IRIS usually occurs within three months of starting ART with high levels of clinical manifestations including lymphadenitis, abscess, and respiratory failure [37].