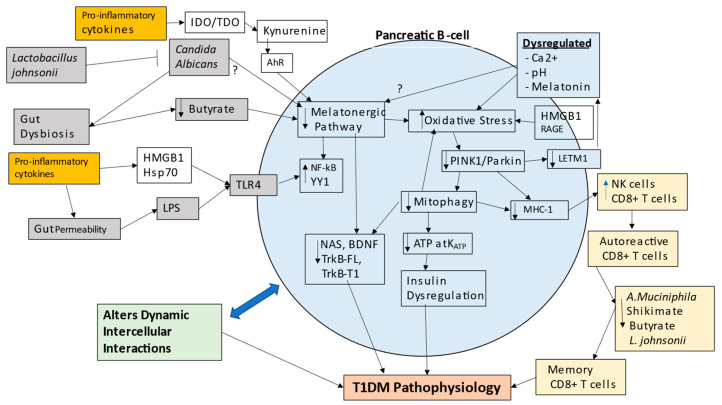
Figure 5.
Shows how gut dysbiosis, gut permeability, pro-inflammatory cytokines, and Candida albicans fungal infection act to suppress the mitochondrial melatonergic pathway in pancreatic β-cells. The suppressed capacity to upregulate melatonin prolongs the heightened activation of pro-inflammatory signaling via the transcription factors, NF-κB and YY1, coupled to decreased activation of TrkB-FL and/or TrkB-T1 by NAS and BDNF. A suppressed mitochondrial melatonergic pathway enhances oxidative stress, thereby decreasing PINK1 and its interactions with parkin and LETM1 on the mitochondrial membrane. Decreased PINK1 suppresses mitophagy, coupled to increased MHC-1 that drives ‘autoimmune’ processes via NK cell and CD8+ T cell attraction. The accompanying decrease in OXPHOS-derived ATP prevent KATP induced insulin, whilst decreased PINK1 attenuates LETM1 phosphorylation, leading to Ca2+ and pH dysregulation, likely accompanied by alterations in how LETM1 interacts with 14-3-3 and/or AANAT in the regulation of the mitochondrial melatonergic pathway. As well as activating TLR4, HMGB1 activates RAGE, thereby further contributing to oxidative stress. Changes in pancreatic β-cell mitochondrial function, including by ROS-driven miRNAs, will change patterned gene induction, with consequent changes in fluxes that mediate pancreatic β-cell interactions with other cells in the pancreatic islet microenvironment, thereby changing the dynamic intercellular interactions occurring. The decrease in shikimate pathway, A. muciniphila, L. johnsonii, and butyrate, contributed to by bacteriophages and enteroviruses, provides ‘bystander’ activation of autoreactive CD8+ T cells—possibly in Peyer’s patches—thereby preventing thymic deselection and driving classical ‘autoimmunity’. Abbreviations: AhR: aryl hydrocarbon receptor; BDNF: brain-derived neurotrophic factor; HMGB: high-mobility group box; hsp: heat shock protein; IDO: indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase; KATP: ATP-activated potassium channel; LETM1: leucine zipper-EF hand-containing transmembrane protein 1; LPS: lipopolysaccharide; MHC-1: major histocompatibility complex-class 1; NAS: N-acetylserotonin; NF-κB: nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; RAGE: receptor for advanced glycation end-products; NK: natural killer; TDO: tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase; TrkB-FL: tyrosine kinase receptor B-full length; TrkB-T1: tyrosine kinase receptor B-truncated; YY1: yin yang 1.