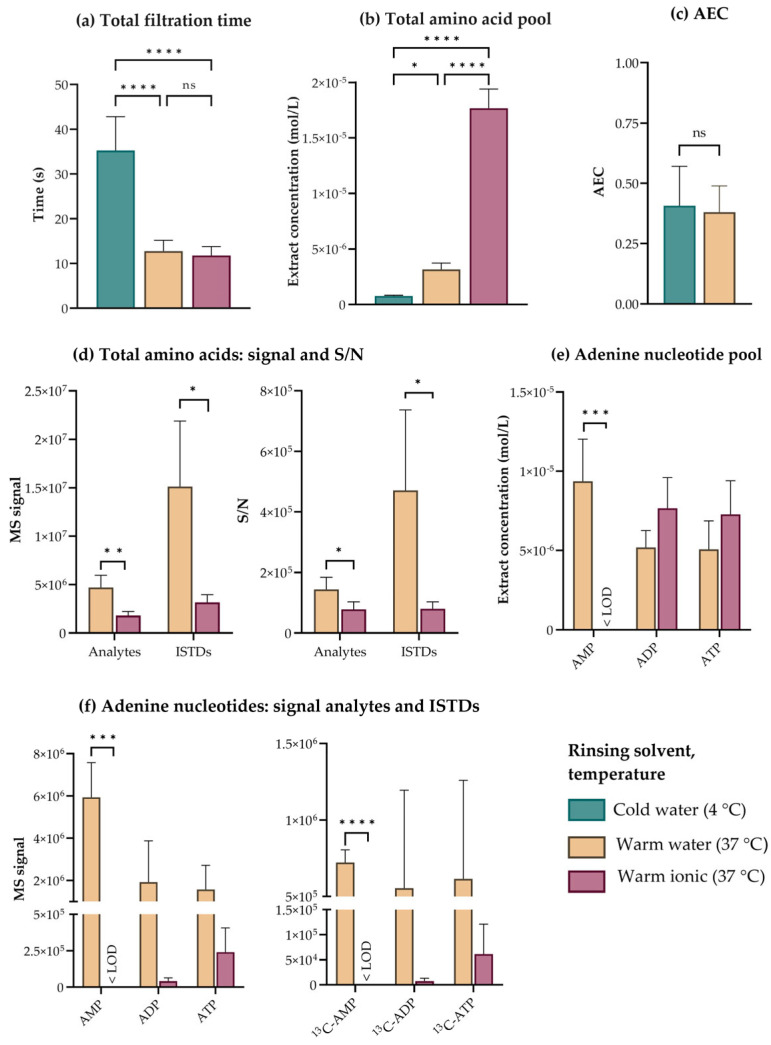
Figure 3.
Effects of rinsing solvent and temperature. (a) Filtration times (s), (b) total amino acid extract concentrations (mol/L), and (c) adenylate energy charges (AECs) as measured for five OD600 units of E. coli rinsed with 10 mL of cold water (4 °), warm water (37 °C), or a warm rinsing solution ionic to the culture medium (37 °C) under a controlled vacuum on polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) filters with a pore size of 0.45 µm. (d) Total mass spectrometric (MS) signal (left panel) and signal-to-noise ratio (S/N) (right panel) of the total amino acid pool and corresponding 13C, (15N)-labeled internal standard (ISTDs), (e) adenine nucleotide extract concentrations (mol/L), and (f) MS signals (left panel) and S/N (right panel) of the adenine nucleotides and corresponding ISTDs, all in five OD600 units of E. coli rinsed with 10 mL of water warm water (37 °C) or a warm rinsing solution ionic to the culture medium (37 °C) under a controlled vacuum on PVDF filters with a pore size of 0.45 µm. The average ± SD of n = 4–8 technical replicates is presented. Significance levels for multiple comparisons from one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons tests (a,b) and for pairwise comparisons are from two-tailed t-test assuming equal variances (c–f), are both marked ns: not significant; *: p≤ 0.05; **: p ≤ 0.01; ***: p ≤ 0.001; ****: p≤ 0.0001. LOD; limit of detection.