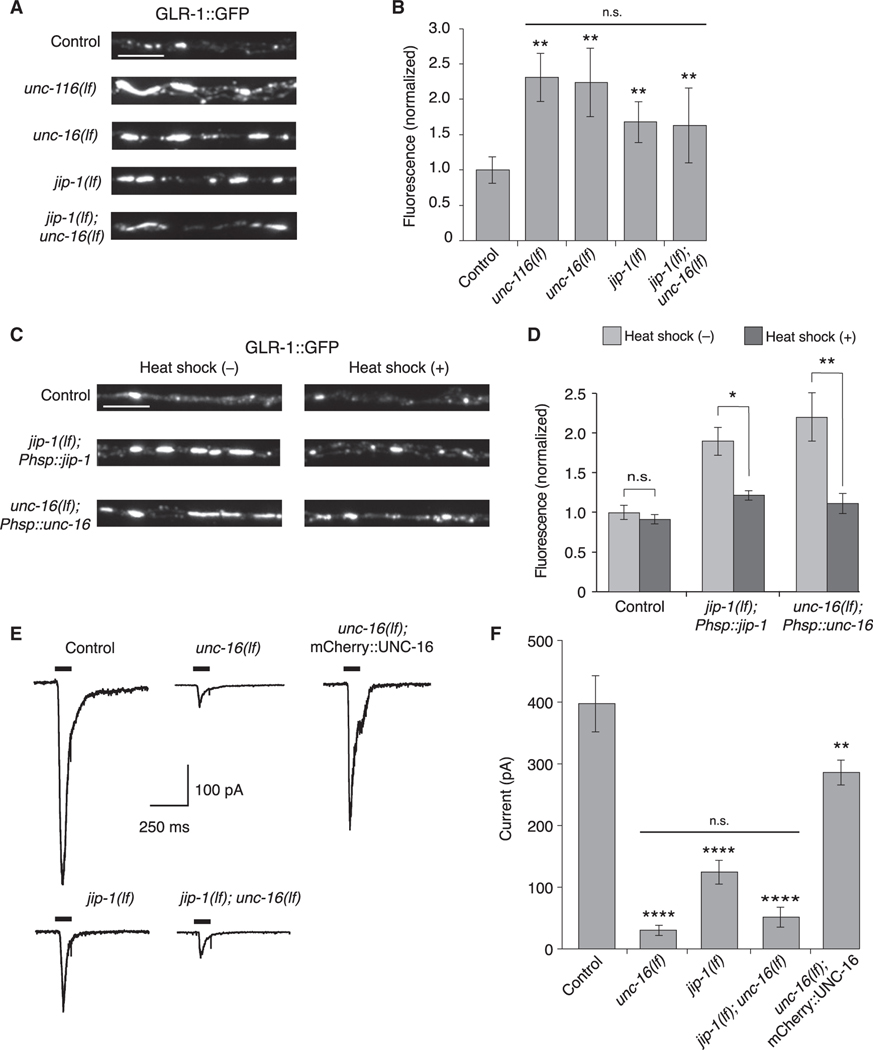
Figure 2. UNC-16 and JIP-1 are required for GLR-1 synaptic levels and function.
(A) Confocal images of GLR-1::GFP puncta in the proximal region of the AVA processes in transgenic control and mutant worms.
(B) GLR-1::GFP fluorescence intensity in the proximal AVA processes in transgenic control (n = 40), unc-116(lf) (n = 20), unc-16(lf) (n = 21), jip-1(lf) (n = 20), and jip-1(lf); unc-16(lf) (n = 20) (normalized to control). **Significantly different from control, p < 0.01. Horizontal bar indicates unc-116(lf), unc-16(lf), and jip-1(lf) single mutants were not significantly different from each other or from the jip-1(lf); unc-16(lf) double mutant (Kruskal-Wallis and Dunn’s multiple testing).
(C) Confocal images of GLR-1::GFP in the proximal AVA processes in transgenic control worms (without Phsp::jip-1 or Phsp::unc-16), and transgenic jip-1(lf) and unc-16(lf) that expressed either Phsp::jip-1 or Phsp::unc-16, respectively and either with or without heat-shock treatment (see STAR Methods).
(D) GLR-1::GFP fluorescence intensity in control worms without (n = 38) or with (n = 29) heat shock, jip-1(lf); Phsp::jip-1 without (n = 30) or with (n = 29) heat shock, and unc-16(lf); Phsp::unc-16 without (n = 28) or with (n = 24) heat shock (normalized to control without heat-shock treatment).*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; n.s., not significant (Kruskal-Wallis and Dunn’s multiple testing).
(E) Currents measured in AVA neurons in response to glutamate application (black bars) in transgenic control and mutant worms. Cells were held at −60 mV.
(F) Peak glutamate-gated current in control (n = 12), unc-16(lf) (n = 8), jip-1(lf) (n = 7), jip-1(lf); unc-16(lf) (n = 3), and transgenic unc-16(lf); mCherry::UNC-16 mutants (n = 4). ****Significantly different from control, p < 0.0001. **Significantly different from unc-16(lf), p < 0.01. Horizontal bar indicates unc-16(lf) and jip-1(lf) single mutants were not significantly different from each other or from the jip-1(lf); unc-16(lf) double mutant (one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni correction).
Scale bars, 5 μm. Error bars represent SEM. See STAR Methods for a description of statistical analysis. See also Figure S3, Tables S1, and S2.