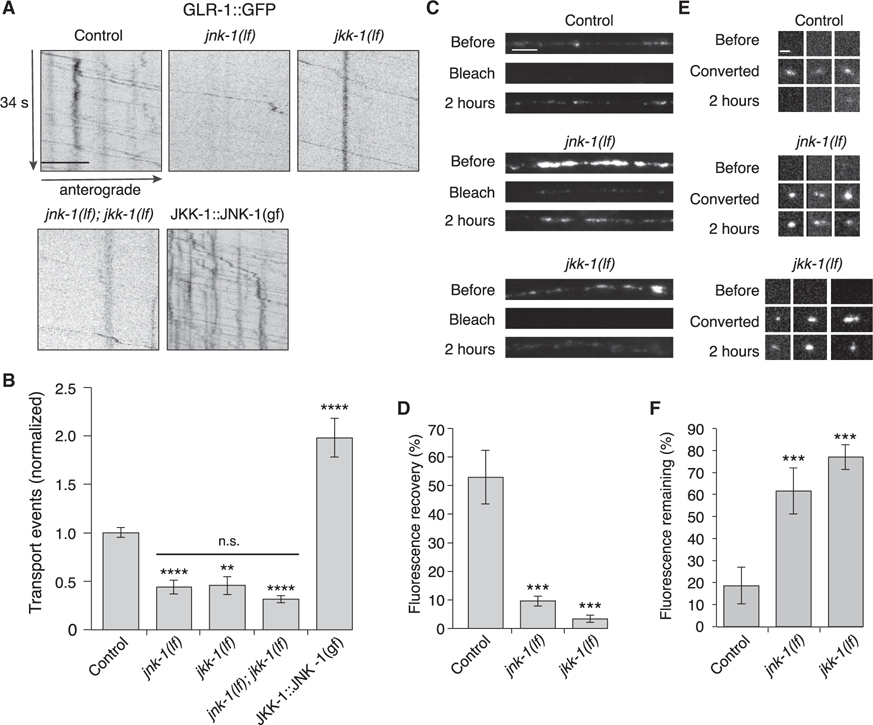
Figure 5. MAPK signaling pathways regulate AMPAR transport and synaptic accumulation.
(A) Kymographs of GLR-1::GFP transport in the AVA processes of transgenic control worms, jnk-1(gk7) and jkk-1(km2) lf mutants, and worms that expressed the JKK-1::JNK-1::TagRFP-T gain-of-function (gf) chimera. Scale bar, 5 μm.
(B) Total GLR-1::GFP transport events in control (n = 13), jnk-1(lf) (n = 8), jkk-1(lf) (n = 11), jnk-1(lf); jkk-1(lf) (n = 9), and JKK-1::JNK-1::TagRFP-T (n = 8) (normalized to control). Significantly different from control, **p < 0.01, and ****p < 0.0001. Horizontal bar indicates jnk-1(lf) and jkk-1(lf) single mutants were not significantly different from each other or from the jnk-1(lf); jkk-1(lf) double mutant (one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison).
(C) Confocal images of GLR-1::GFP in the distal AVA processes of transgenic control and mutant worms before, immediately after (bleach), and 2 h after photobleaching. Scale bar, 5 μm.
(D) GLR-1::GFP fluorescence recovery 2 h after photobleaching in control (n = 7), jnk-1(lf) (n = 8), and jkk-1(lf) (n = 8) as a percentage of the fluorescent signal before photobleaching.
(E) Confocal images of GLR-1::Dendra2 puncta (three examples per genotype) before, immediately after (converted), and 2 h after photoconverting GLR-1::Dendra2 from green to red fluorescence (red channel only). Scale bar, 1.3 μm.
(F) The percentage of red fluorescence remaining 2 h after photoconverting GLR-1::Dendra2 in control (n = 10), jnk-1(lf) (n = 9), and jkk-1(lf) (n = 10). ***Significantly different from same-day controls, p < 0.001.
All strains carried the glr-1(ky176) deletion mutation (see STAR Methods). Error bars represent SEM. See STAR Methods for a description of statistical analysis. See also Figure S6, Tables S1, and S2.